F5 Solutions for Containers > Appendix > Appendix 2: Build a Kubernetes Cluster Source | Edit on
Lab 2.4 - Setup the Kubernetes UI¶
Important
The following commands need to be run on the master only.
Note
You have two options to install the UI:
- Run the included script from the cloned git repo.
- Manually run each command.
Both options are included below.
“git” the demo files
Note
These files should be here by default, if NOT run the following commands.
git clone -b develop https://github.com/f5devcentral/f5-agility-labs-containers.git ~/agilitydocs cd ~/agilitydocs/kubernetes
Run the following commands to configure the UI
Note
A script is included in the cloned git repo from the previous step. In the interest of time you can simply use the script.
cd /home/ubuntu/agilitydocs/kubernetes ./create-kube-dashboard
or run through the following steps:
kubectl create serviceaccount kubernetes-dashboard -n kube-system kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubernetes-dashboard --clusterrole=cluster-admin --serviceaccount=kube-system:kubernetes-dashboard
Warning
These commands create a service account with full admin rights. In a typical deployment this would be overkill.
Create a file called kube-dashboard.yaml with the following content:
1# ------------------- Dashboard Deployment ------------------- # 2 3kind: Deployment 4apiVersion: apps/v1beta2 5metadata: 6 labels: 7 k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard 8 name: kubernetes-dashboard 9 namespace: kube-system 10spec: 11 replicas: 1 12 revisionHistoryLimit: 10 13 selector: 14 matchLabels: 15 k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard 16 template: 17 metadata: 18 labels: 19 k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard 20 spec: 21 containers: 22 - name: kubernetes-dashboard 23 image: k8s.gcr.io/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.10.1 24 ports: 25 - containerPort: 9090 26 protocol: TCP 27 args: 28 # Uncomment the following line to manually specify Kubernetes API server Host 29 # If not specified, Dashboard will attempt to auto discover the API server and connect 30 # to it. Uncomment only if the default does not work. 31 # - --apiserver-host=http://my-address:port 32 volumeMounts: 33 # Create on-disk volume to store exec logs 34 - mountPath: /tmp 35 name: tmp-volume 36 livenessProbe: 37 httpGet: 38 path: / 39 port: 9090 40 initialDelaySeconds: 30 41 timeoutSeconds: 30 42 volumes: 43 - name: tmp-volume 44 emptyDir: {} 45 serviceAccountName: kubernetes-dashboard 46 # Comment the following tolerations if Dashboard must not be deployed on master 47 tolerations: 48 - key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master 49 effect: NoSchedule 50 51--- 52# ------------------- Dashboard Service ------------------- # 53 54kind: Service 55apiVersion: v1 56metadata: 57 labels: 58 k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard 59 name: kubernetes-dashboard 60 namespace: kube-system 61spec: 62 ports: 63 - port: 80 64 targetPort: 9090 65 type: NodePort 66 selector: 67 k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
Apply Kubernetes manifest file:
kubectl apply -f kube-dashboard.yaml
To access the dashboard, you need to see which port it is listening on. You can find this information with the following command:
kubectl describe svc kubernetes-dashboard -n kube-system
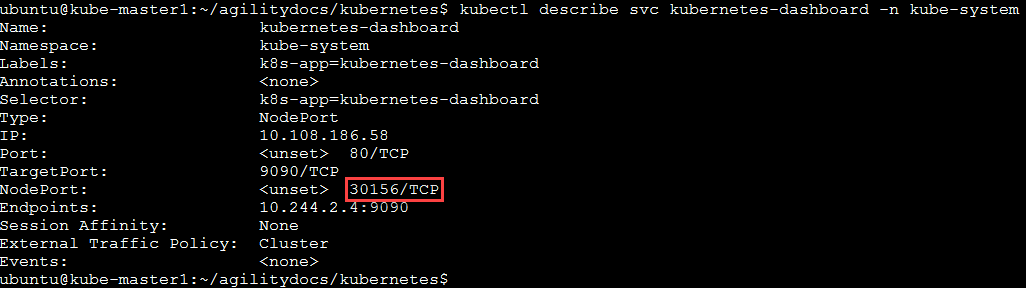
Note
In our service we are assigned port “30156” (NodePort), you’ll be assigned a different port.
We can now access the dashboard by connecting to the following uri http://10.1.1.7:30156