Optimize hypervisor settings¶
The following procedure is an example process for updating settings in the VMware hypervisor. You can make similar setting changes in all supported, on-prem hypervisors.
Determine the NUMA (CPU) associated with the PCIe slot in which the NIC is installed.
On a dual CPU 24 core system, 48 CPUs are available (example using a Xeon 8260).
- If the NIC is on NUMA 0, then utilize CPUs 0-23 (HT OFF) | 0-47 (HT ON).
- If the NIC is on NUMA 1, then utilize CPUs 24-47 (HT OFF) | 48-95 (HT ON).
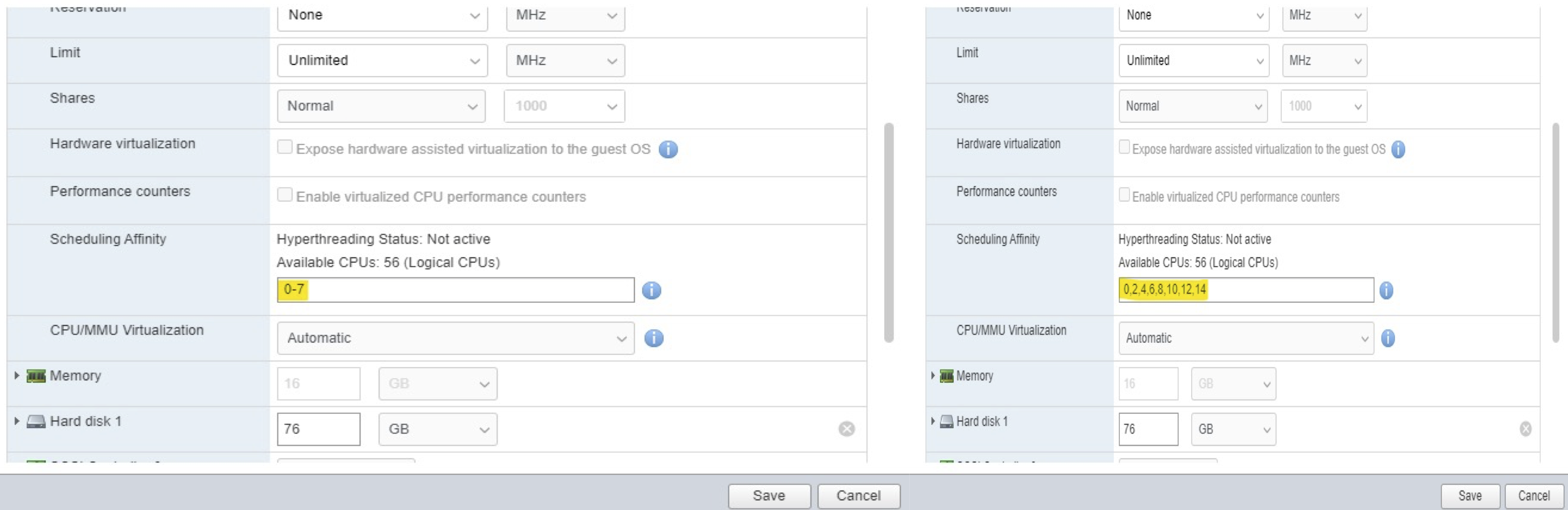
To pin vCPUs under VMware; edit the VM, expand the CPU section; scroll down to Scheduling Affinity and pin the CPU cores matching the NUMA in Step 2:
- Eight vCPU example with HT OFF on left (you can use a range).
- Eight vCPU example on right with HT ON (must pin every other core).
Change the ctxPerDev parameter to modify the number of NIC queues:
- val = “1” - Spawns a per vNIC thread in VMM for Tx scaling.
- val = “3” - Spawns a per queue per vNIC thread in VMM for Tx scaling.
Best practices for deploying BIG-IP VE on VMware¶
When deploying BIG-IP® Virtual Edition (VE) on a VMware host, use these best practices.
| Issue | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Redundant system configuration | Run the two units of an active-standby pair on separate physical hosts. You can accomplish this in two ways: either manually create a virtual machine peer on each host, or, if you are using VMware Dynamic Resource Scheduler (DRS), create a DRS rule with the option Separate Virtual Machine that includes each unit of the BIG-IP® VE redundant pair. |
| Live migration of BIG-IP VE virtual machines | Perform live migration of BIG-IP VE virtual machines on idle BIG-IP VE virtual machines only. Live migration of BIG-IP VE while the virtual machine is processing traffic could produce unexpected results. |
| VMware DRS environments | In DRS environments, perform live migration of BIG-IP VE virtual machines (using VMware vMotion) on idle BIG-IP VE virtual machines only. Live migration of BIG-IP VE while the virtual machine is processing traffic could produce unexpected results. Disable automatic migrations by adjusting the DRS Automation Level to Partially Automated, Manual, or Disabled on a per BIG-IP VE basis. |
| Resource reservations | Default BIG-IP VE behavior is deployed with a 2000 or 4000 MHz CPU, and 2, 4, or 8 GB of memory reservation. Together, these reservations typically prevent system instability on heavily loaded hosts and are considered minimal. The CPU reservation can be up to 100 percent of the defined virtual machine hardware. For example, if the hypervisor has a 3 GHz core speed, the reservation of a virtual machine with 2 CPUs can be only 6 GHz or less. |
| Disable hyper-threading on older processors | F5 Networks recommends turning off Hyper-Threading Technology when using host machines with Intel Pentium 4 era processors. Doing so will prevent possible timing issues with BIG-IP VE. Important: Production licenses are not supported on Pentium 4 processors. |