Google Cloud Platform: Single NIC config sync¶
The following diagram shows a basic deployment of two BIG-IP VE instances in two separate zones. Each zone is in a different physical location, which helps ensure that your application remains available if one zone becomes unavailable.
In this deployment, the two BIG-IP VEs are synchronizing their configurations to one another; they are not communicating for the purpose of failover.
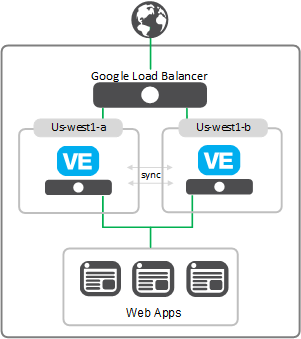
This deployment has the following benefits:
- The two BIG-IP VEs are on different hardware, because they are in separate zones, and as such, both servers should not be down at the same time.
- BIG-IP VE copies changes from one BIG-IP VE to the other through config sync.
- If one BIG-IP VE fails, the other BIG-IP VE continues to process traffic, though the failed system drops the packets.
- Both BIG-IP VEs have Active status and are available to process traffic.
- BIG-IP VE can process more traffic; if each BIG-IP VE has 1 Gbps of throughput, then together they have 2 Gbps.
Configure config sync on Google Cloud Platform¶
Before you can complete this task:
- Both BIG-IP VEs must be running the same version of BIG-IP VE system software.
- The BIG-IP VEs must not use the same device name. To view the name, use the tmsh command:
list /cm device. The device name is in the first line, for examplecm device bigip1 {. To change the name, usemv cm device <current_device_name> <new_device_name>. - Firewall rules must allow traffic to port 4353 and 6699.
Enable config sync communication when you want to automatically or manually synchronize configuration information.
Note: The following steps apply to a single-NIC configuration only.
Use an SSH tool to connect to each of the BIG-IP VEs.
Ensure that you are at the tmsh prompt.
tmshOn each BIG-IP VE, disable functionality that enforces single NIC setup.
modify sys db provision.1nicautoconfig value disableConfirm that the value is correct by typing:
list sys db provision.1nicautoconfigThe return value should be:
value "disable".If the BIG-IP VE instances are in different zones (us-west1-a and us-west1-b, for example), you must move your default gateway to a different partition by completing the following tasks on each BIG-IP VE.
View the existing routes and note the IP addresses.
list net routeDelete the default route.
delete net route defaultDelete dhclient_route1.
delete net route dhclient_route1Create a new partition.
create sys folder /LOCAL_ONLY device-group none traffic-group traffic-group-local-onlyCreate dhclient_route1 in the new partition.
create net route /LOCAL_ONLY/dhclient_route1 network <gateway_ip_address>/32 interface /Common/internalCreate the default route in the new partition.
create net route /LOCAL_ONLY/default network default gw <route_IP_address>Save the configuration.
save sys configChange to the LOCAL_ONLY partition and confirm the route.
cd /LOCAL_ONLY list net route
Change back to the Common partition.
cd /Common
Set up device trust and config sync.
On each BIG-IP VE, specify the static private IP address of the BIG-IP VE itself.
modify cm device <device_name> configsync-ip <private_ip_address>Establish device trust: On one BIG-IP VE, enter the static private IP address of the other BIG-IP VE, along with its user name and password.
modify cm trust-domain add-device { ca-device true device-ip <peer_ip_address> device-name <peer_device_name> username <peer_username> password <peer_password> }On the same BIG-IP VE as the previous step, create a sync-failover device group with network failover disabled.
create cm device-group <device_group_name> devices add { <all-bigip-device-names-separated-by-space> } type sync-failover auto-sync enabled network-failover disabledSync the BIG-IP VE to the other BIG-IP VE.
run cm config-sync to-group <device_group_name>
The BIG-IP VEs are now in sync.