Ingress¶
Overview of Ingress¶
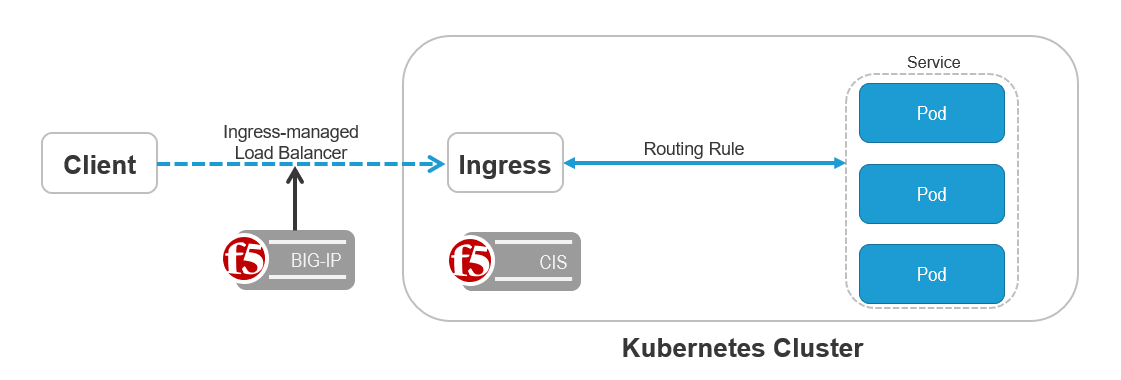
Ingress exposes HTTP and HTTPS routes from outside the cluster to services within the cluster. Traffic routing is controlled by rules defined on the Ingress resource.
Here is a simple diagram where an Ingress sends all its traffic to one Service:
See also
Refer to Kubernetes Ingress documentation and Ingress v1 networking.k8s.io for more information.
Why use Ingress?
You can use Ingress to make internal services reachable from outside the cluster. It saves static IPs, as you will not need to declare multiple LoadBalancer services.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: test-ingress spec: ingressClassName: f5 rules: - http: paths: - path: /testpath pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: test port: number: 80 |
As with all other Kubernetes resources, an Ingress needs apiVersion, kind, and metadata fields.
The Ingress spec has all the information needed to configure a load balancer or proxy server. Most importantly, it contains a list of rules matched against all incoming requests. Ingress resource only supports rules for directing HTTP traffic.
Ingress Rules:
Each HTTP rule contains the following information:
- An optional host. In this example, no host is specified, so the rule applies to all inbound HTTP traffic through the IP address specified. If a host is provided (for example, foo.bar.com), the rules apply to that host.
- A list of paths (for example,
/testpath), each of which has an associated backend defined with aserviceNameandservicePort. Both the host and path must match the content of an incoming request before the load balancer directs traffic to the referenced Service. - A backend is a combination of Service and port names. HTTP (and HTTPS) requests to the Ingress that match the host and path of the rule are sent to the listed backend.
Default backend:
An Ingress with no rules sends all traffic to a single default backend. The default backend is typically a configuration option of the Ingress controller and is not specified in your Ingress resources.
If none of the hosts or paths match the HTTP request in the Ingress objects, the traffic is routed to your default backend.
Path types:
Each path in an Ingress has a corresponding path type. There are three supported path types:
- Default: With this path type, matching is up to the IngressClass. Implementations can treat this as a separate pathType or treat it identically to prefix or
Exactpath types. - Exact: Matches the URL path exactly and with case sensitivity.
- Prefix: Matches based on a URL path prefix split by /. Matching is case sensitive and done on a path element-by-element basis. A path element refers to the list of labels in the path split by the / separator. A request is a match for path p if every p is an element-wise prefix of p of the request path.
IngressClass Support
In a Kubernetes cluster, there might be multiple ingress controllers and you need to have a way to associate a particular ingress resource with an ingress controller.
Specify the ingress controller that should handle the ingress resource by using the ingressClassName in your ingress resource. Each ingress resource can be associated with only one ingressClassName.
You can use the annotation ingressclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class to set the annotation as true to make CIS the default ingress controller of k8s cluster.
Note
For f5 ingress class, IngressClass.spec.controller must always be f5.com/cntr-ingress-svcs. CIS verifies this controller name while processing the ingress resources.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: IngressClass metadata: name: f5 annotations: # Set the annotation as true to make CIS default ingress controller of k8s cluster ingressclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true" spec: # Provide the controller name as "f5.com/cntr-ingress-svcs" # Warning: don't change the controller name as cis verify the controller name while processing the ingress resource controller: f5.com/cntr-ingress-svcs |
Types of Ingress¶
Note
See Ingress examples on GitHub <https://github.com/F5Networks/k8s-bigip-ctlr/tree/2.x-master/docs/config_examples/ingress> for the most recent versions of these examples.
Single Service Ingress: You can expose a single service by specifying default backend with no rules. For example:
The most up-to-date version of this example is here: single-service-ingress.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress1 namespace: default annotations: # Provide an IP address from the external VLAN on your BIG-IP device virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "10.190.25.70" spec: defaultBackend: service name: myService port: number: 80
Simple Fanout: A fanout configuration routes traffic from a single IP address to more than one Service, based on the HTTP URI being requested.
The most up-to-date version of this example is here: simple-ingress-fanout.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingress-fanout namespace: default annotations: # IP address of a BIG-IP pool member virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "101.10.10.20" # Load balancing algorithm virtual-server.f5.com/balance: "round-robin" spec: rules: - host: mysite.example.com http: paths: - path: /foo pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: service1 port: number: 4200 - path: /bar pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: service2 port: number: 8080
Name Based Virtual Hosting: Name-based virtual hosts support routing HTTP traffic to multiple host names at the same IP address.
The most up-to-date version of this example is here: name-based-ingress.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ing-virtual-hosting namespace: default annotations: # BIG-IP pool member IP address virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "10.10.10.20" # Load balancing algorithm virtual-server.f5.com/balance: "round-robin" # Specify the port you want to handle requests virtual-server.f5.com/http-port: "80" spec: ingressClassName: f5 rules: # URL - host: mysite.example.com http: # path to Service from URL paths: - path: /myApp1 backend: service: name: myService1 port: number: 80 # URL - host: yoursite.example.com http: # path to Service from URL paths: - path: /myApp2 backend: service: name: myService2 port: number: 80
Note
CIS does not support Ingress hostname with wildcards. For example:
host: "*.example.com"
TLS: You can secure an Ingress by specifying a Secret that contains a TLS private key and certificate. Currently the Ingress only supports a single TLS port, 443, and assumes TLS termination.
The TLS secret must contain keys named
tls.crtandtls.keythat contain the certificate and private key to use for TLS. For example:The most up-to-date version of this example is here: example-secret-tls.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: example-secret-tls namespace: default data: tls.crt: base64 encoded cert tls.key: base64 encoded key type: kubernetes.io/tls
Referencing this secret in an Ingress tells the Ingress controller to secure the channel from the client to the load balancer using TLS. You need to make sure the TLS secret you created came from a certificate that contains a Common Name (CN), also known as a Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) for
example.comThe most up-to-date version of this example is here: single-service-tls-ingress.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingressWithK8sSecret namespace: default annotations: # Provide an IP address for the BIG-IP pool you want to handle traffic. virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "10.10.10.20" spec: # Provide the IngressClassName as "f5" ingressClassName: f5 tls: - hosts: - mysite.foo.com #Referencing this secret in an Ingress tells the Ingress controller to #secure the channel from the client to the load balancer using TLS secretName: example-secret-tls rules: - host: mysite.foo.com http: paths: - path: / pathType: ImplementationSpecific backend: service: name: svc port: number: 80
BIG-IP CLientSSL profiles can be atttached to Ingress resources as shown below.
single-service-tls-ingress.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ingressTLS namespace: default annotations: # Provide an IP address for the BIG-IP pool you want to handle traffic. virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "10.10.10.20" # Allow/deny TLS connections ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true" # Allow/deny HTTP connections ingress.kubernetes.io/allow-http: "false" # Specify an already-configured SSL Profile on BIG-IP that should be # used for this Ingress. Annotation is available for CIS 2.5 and above. # Follows the format "/partition/profile_name". virtual-server.f5.com/clientssl: '[ { "hosts": [ "https-example.foo.com" ], "bigIpProfile": "/Common/clientssl" } ]' spec: # Provide the IngressClassName as "f5" ingressClassName: f5 rules: - host: https-example.foo.com http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: svc port: number: 80
- Load balancing: An Ingress controller is bootstrapped with some load balancing policy settings that it applies to all Ingress, such as the load balancing algorithm, backend weight scheme, and others. More advanced load balancing concepts (e.g. persistent sessions, dynamic weights) are not yet exposed through the Ingress. You can instead get these features through the load balancer used for a Service.
How to deploy Ingress¶
Prerequisites¶
In order to deploy Ingress, you must have the following:
- An Ingress controller to satisfy an Ingress. Only creating an Ingress resource has no effect.
- Use F5 BIG-IP Container Ingress Services (CIS) as your Ingress Controller. It must be up and running.
- When using networking.k8s.io/v1 API version for Ingress, create an IngressClass for CIS controller. Add networking.k8s.io/v1 to ClusterRole.
Quickstart¶
Create an Ingress resource. In this example, we create two services to demonstrate how the Ingress routes our request. We run two web applications that output a slightly different response.
kind: Pod apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: foo-app labels: app: foo spec: containers: - name: foo-app image: f5/img args: - "-text=foo" --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: foo-service spec: selector: app: foo ports: - port: 5678 # Default port for image
kind: Pod apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: bar-app labels: app: bar spec: containers: - name: bar-app image: f5/img args: - "-text=bar" --- kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: bar-service spec: selector: app: bar ports: - port: 5678 # Default port for image
Create the resources:
$ kubectl apply f foo-app.yaml $ kubectl apply f bar app.yaml
Declare an Ingress to route requests to
/footo the first service, and requests to/barto the second service:apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: example-ingress annotations: ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: / spec: ingressClassName: f5 rules: - http: paths: - path: /foo backend: service name: foo-service port: number: 5678 - path: /bar backend: service name: bar-service port: number: 5678
Note
Inside your Ingress configuration you can only redirect to services in the same namespace.
Create the Ingress in the cluster:
kubectl create -f ingress.yaml
Verify that it is working:
$ curl -kL http://localhost/foo foo $ curl -kL http://localhost/bar bar $ curl -kL http://localhost/notfound default backend - 404
Ingress Resources¶
Supported Ingress Annotations¶
| Annotation | Type | Required | Description | Default | Allowed Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| virtual-server.f5.com/ip | string | Required | The IP address you want to assign to the virtual server. You can specify the IPv4
address with CIDR slash notation.
Set to controller-default if you want to use the default-ingress-ip
specified in the Configuration Parameters above. |
N/A |
|
|
| virtual-server.f5.com/partition | string | Optional | The BIG-IP partition in which the Controller should create/update/delete objects for this Ingress. | N/A | BIG-IP AS3 agent does not support write to “Common” partition | |
| kubernetes.io/ingress.class | string | Optional | Tells the Controller it should only manage Ingress resources in the f5 class.
If defined, the value must be f5. |
f5 | f5 |
|
| virtual-server.f5.com/balance | string | Optional | Sets the load balancing mode. | round-robin | Any supported load balancing algorithm. | |
| virtual-server.f5.com/http-port | integer | Optional | Specifies the HTTP port. | 80 | ||
| virtual-server.f5.com/https-port | integer | Optional | Specifies the HTTPS port. | 443 | ||
| virtual-server.f5.com/health | JSON object | Optional | Defines a health monitor for the Ingress resource. | N/A | ||
| path | string | Required | The path for the Service specified in the Ingress resource. | N/A | ||
| interval | integer | Required | The interval at which to check the health of the virtual server. | N/A | ||
| timeout | integer | Required | Number of seconds before the check times out. | N/A | ||
| send | string | Required | The send string to set in the health monitor. | N/A | ||
| recv | string | Optional | String or RegEx pattern to match in first 5,120 bytes of backend response. | N/A | ||
| type | string | Optional | Health monitor type. Typically http or https. | http | ||
| sslProfile | string | Optional | Server SSL profile for https health monitor. | N/A | Only ssl profiles created in Common
partition can be specified.
For example: /Common/serverssl |
|
| ingress.kubernetes.io/allow-http | boolean | Optional | Tells the Controller to allow HTTP traffic for HTTPS Ingress resources. | false | true, false |
|
| ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect | boolean | Optional | Tells the Controller to redirect HTTP traffic to the HTTPS port for HTTPS Ingress resources (see TLS Ingress resources, below). | true | true, false |
|
| virtual-server.f5.com/serverssl | string | Optional | The name of a pre-configured server ssl profile on the BIG-IP system. | N/A | ||
| virtual-server.f5.com/clientssl | string | Optional | List of a BIGIP Client SSL profiles. Supported from CIS 2.5 and above. Annotation supported for Ingress resource in networking.k8s.io/v1. | N/A | ||
| virtual-server.f5.com/rewrite-app-root | string | Optional | Root path redirection for the application. | N/A | ||
| virtual-server.f5.com/rewrite-target-url | string | Optional | URL host, path, or host and path to be rewritten. | N/A | ||
| virtual-server.f5.com/allow-source-range | string | Optional | Comma separated list of CIDR addresses to allow inbound to Ingress services. | N/A | Comma separated, CIDR formatted, IP addresses. For example: |
|
| virtual-server.f5.com/translate-server-address | boolean | Optional | Enable/Disable Address Translation. | “true” | "true", "false" |
|
Netmask for Virtual Server for Ingress¶
To configure netmask for Virtual server for Ingress resource, define the virtual-server.f5.com/ip annotation in CIDR slash notation.
For example:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
# Virtual server IP address with CIDR
virtual-server.f5.com/ip: 10.8.0.4/31
name: ingress-svc-foo
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- host: foo.com
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: svc-1
port:
number: 80
path: /foo
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls:
- secretName: foo-secret
Ingress Health Monitors¶
To configure health monitors on your Ingress resource, define the virtual-server.f5.com/health annotation with a JSON object.
Provide an array for each path specified in the Ingress resource.
See the ingress-with-health-monitors-sslprofile.yaml example on GitHub.
Use a BIG-IP SSL profile or Secret¶
You can secure an Ingress using BIG-IP SSL profiles or Kubernetes Secrets.
- Specify the SSL profile(s) or the Secret containing the cert and key in the
spec.tlssection of the Ingress resource. - Add the
ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirectannotation (OPTIONAL; defaults to"true"). - Add the
ingress.kubernetes.io/allow-httpannotation (OPTIONAL; defaults to"false").
Note
- You can specify one or more SSL profiles in your Ingress resource.
- If you specify a
spec.tlssection without providing the TLS Ingress properties, the BIG-IP device uses its local traffic policies to redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS.
The table below shows how the Controller behaves for different combinations of the ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect and ingress.kubernetes.io/allow-http settings.
| State | sslRedirect | allowHttp | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F | F | Just HTTPS, nothing on HTTP |
| 2 | T | F | HTTP redirects to HTTPS |
| 2 | T | T | Honor sslRedirect == true |
| 3 | F | T | Both HTTP and HTTPS |
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingressTLS
annotations:
virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "101.10.10.20"
ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
ingress.kubernetes.io/allow-http: "false"
virtual-server.f5.com/clientssl: '[ { "bigIpProfile": "/Common/clientssl" } ]'
spec:
ingressClassName: f5
defaultBackend:
# Provide the name of a single Kubernetes Service you want to expose to external
# traffic using TLS
service:
name: myService
port:
number: 443
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingressTLS
namespace: default
annotations:
virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "10.10.10.20"
ingress.kubernetes.io/ssl-redirect: "true"
ingress.kubernetes.io/allow-http: "false"
spec:
ingressClassName: f5
tls:
# Provide the name of the Secret you want to use.
- secretName: myTLSSecret
backend:
# Provide the name of a single Kubernetes Service you want to expose to external
# traffic using TLS
service:
name: myService
port:
number: 443
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: no-rules-map
spec:
ingressClassName: f5
tls:
- secretName: testsecret
backend:
service:
name: s1
port:
number: 80
f5-k8s-ingress-tls-secret.yaml
See also
Refer to the Kubernetes TLS Ingress documentation for details regarding supported port(s) and termination.
Exposing Headless Service using Ingress¶
You can expose a Kubernetes headless service using ingress as shown in the example below.
Note
- IP addresses specified in the endpoints yaml file can be external or pod IP addresses, which need to be updated manually.
- You can only add the IP addresses in the endpoints; host-names are not supported.
- You can only expose headless service when CIS is deployed in ClusterIP mode.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Endpoints
metadata:
labels:
headless-app: app-1
name: svc-1
subsets:
- addresses:
# Following ip addresses can be external or pod IP Addresses, which needs to be updated manually
- ip: 192.168.0.101
nodeName: node-1
- ip: 192.168.0.102
nodeName: node-2
- ip: 192.168.0.103
nodeName: node-3
ports:
- name: port-app-1
port: 8080
protocol: TCP
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc-1
labels:
headless-app: app-1
spec:
# Specify clusterIP as None to create a headless service
clusterIP: None
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
name: port-app-1
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: svc-1-ingress
annotations:
virtual-server.f5.com/balance: least-connections-node
virtual-server.f5.com/ip: 10.8.10.3
spec:
ingressClassName: f5
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service
name: svc-1
port:
number: 8080
sample-headless-service-ingress.yaml
See also
Refer to the Kubernetes Headless Service documentation .
MultiPartition Support using Ingress Annotation¶
Ingress now supports the MultiPartition feature, where the user can provision BIG-IP in multiple partitions. This helps to easily manage the bigipConfig among the partitions. The MultiPartition feature also helps to improve performance, as CIS processes only the partition when there is a change, instead of sending a unified AS3 declaration to all of the partitions on the BIG-IP every time a change/event is detected.
CIS processes multiple tenant information and still sends the single unified declaration to BIG-IP to avoid multiple posts to BIG-IP for the first time.
Note
The AS3 post call is formed as mgmt/shared/appsvcs/declare/tenant1,tenant2.
This feature is enabled by using ingress annotation virtual-server.f5.com/partition.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: ing-fanout namespace: default annotations: # Provide an IP address for the BIG-IP Virtual Server. virtual-server.f5.com/ip: "1.2.3.4" # Specify the BIG-IP partition containing the virtual server. virtual-server.f5.com/partition: "k8s" # Load balancing algorithm virtual-server.f5.com/balance: "round-robin" # Partiton annotation virtual-server.f5.com/partition: "dev" spec: # Provide the IngressClassName as "f5" ingressClassName: f5 rules: - host: mysite.example.com http: paths: - path: /mysite/app1 pathType: ImplementationSpecific backend: service: name: svc-1 port: number: 80 - path: /mysite/app2 pathType: ImplementationSpecific backend: service: name: svc-2 port: number: 80 |
Examples Repository¶
Note
To provide feedback on Container Ingress Services or this documentation, please file a GitHub Issue.