F5 Solutions for Containers > Appendix > Appendix 6: Build a Mesos / Marathon Cluster Source | Edit on
Lab 2.2 - Setup the Master¶
Important
The following commands need to be run on the master only unless otherwise specified.
Install Mesos, Marathon and Zookeeper¶
Add the mesos/marathon repo
Run the following commands:
apt-key adv --keyserver keyserver.ubuntu.com --recv E56151BF cat <<EOF >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mesosphere.list deb http://repos.mesosphere.com/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) main EOF
Install the mesos, marathon and zookeeper packages
apt update && apt install mesos marathon zookeeperd -y
Setup Zookeeper¶
Note
2181 is zookeeper’s default port.
Setup a unique ID per zookeeper instance. Update
/etc/zookeeper/conf/myidto1,2or3depending on the number of master nodes. In our case1echo 1 > /etc/zookeeper/conf/myid
Modify the zookeeper config file on each master
sed -i /^#server.1/s/#server.1=zookeeper1/server.1=10.2.10.21/ /etc/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg
Setup Mesos¶
Create mesos ip file /etc/mesos-master/ip
echo "10.2.10.21" > /etc/mesos-master/ip
Create mesos hostname file /etc/mesos-master/hostname (specify the IP address of your node)
echo "10.2.10.21" > /etc/mesos-master/hostname
Change the quorum value to reflect our cluster size. It should be set over 50% of the number of master instances. In this case it should be
1because we have only one masterecho 1 > /etc/mesos-master/quorum
Point zookeeper to the master instance. This is done in the file /etc/mesos/zk
echo "zk://10.2.10.21:2181/mesos" > /etc/mesos/zk
Setup Marathon¶
First we need to specify the zookeeper masters that marathon will connect to (for information and things like scheduling). We can copy the previous file we setup for mesos:
echo "MARATHON_MASTER=`cat /etc/mesos/zk`" > /etc/default/marathon
We also need to have marathon store its own state in zookeper (since it runs on all three masters):
echo "MARATHON_ZK=zk://10.2.10.21:2181/marathon" >> /etc/default/marathon
Start your services¶
When you install mesos, the master and slave services are enabled (called mesos-master and mesos-slave). Here, we want our master to focus on this tasks so we need to disable the slave service. Do this on all the master nodes:
systemctl stop mesos-slave echo manual > /etc/init/mesos-slave.override
We need to restart zookeeper and start mesos-master and marathon process on all master nodes:
systemctl restart zookeeper systemctl start mesos-master systemctl enable mesos-master systemctl start marathon
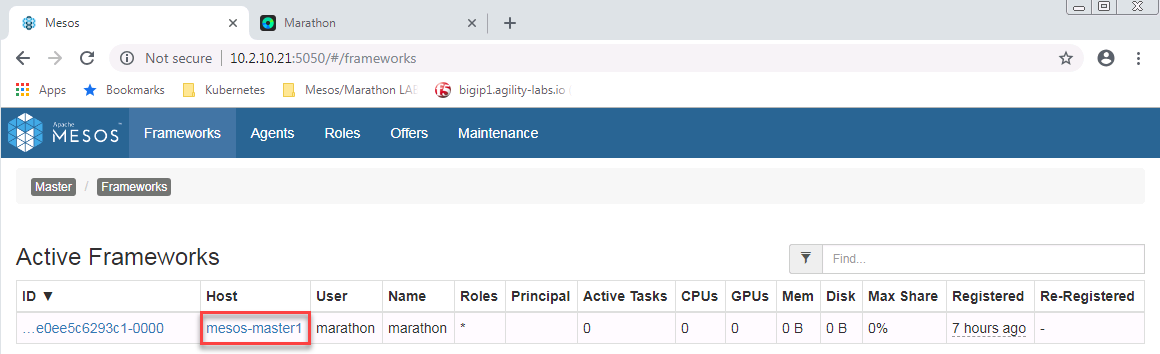
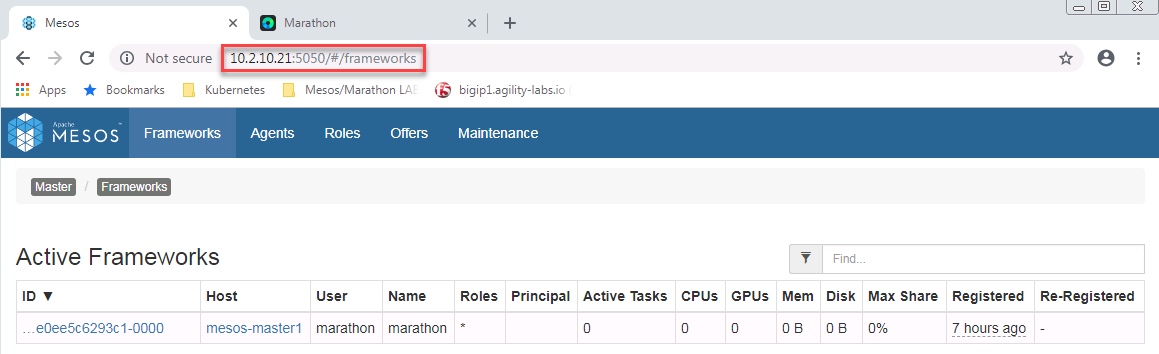
We can validate that it works by connecting to mesos and marathon via a browser. Mesos runs on port 5050 (http) and marathon runs on port 8080 (http).
Mesos:
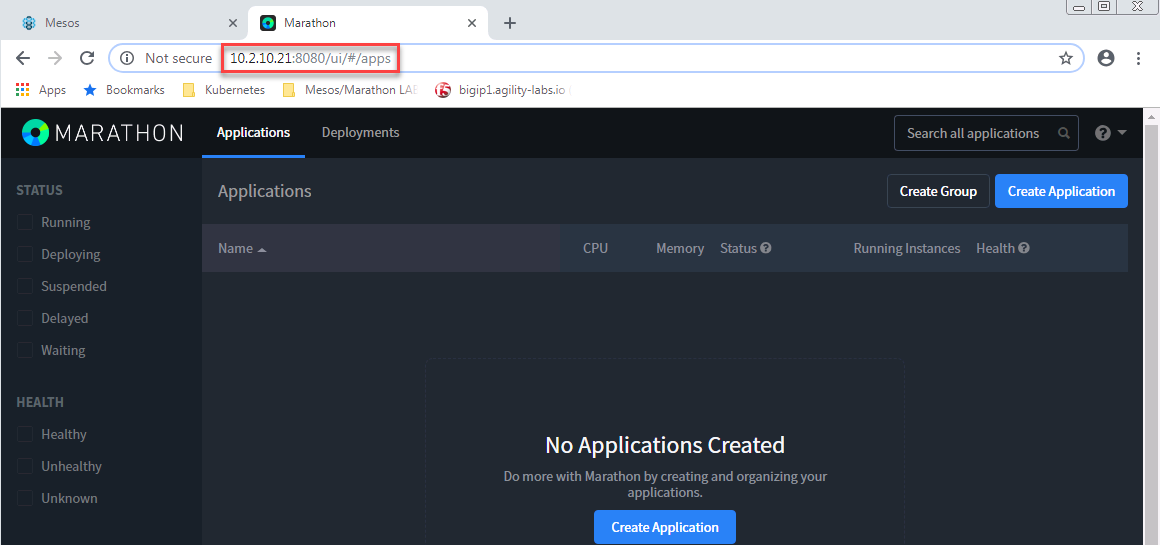
Marathon:
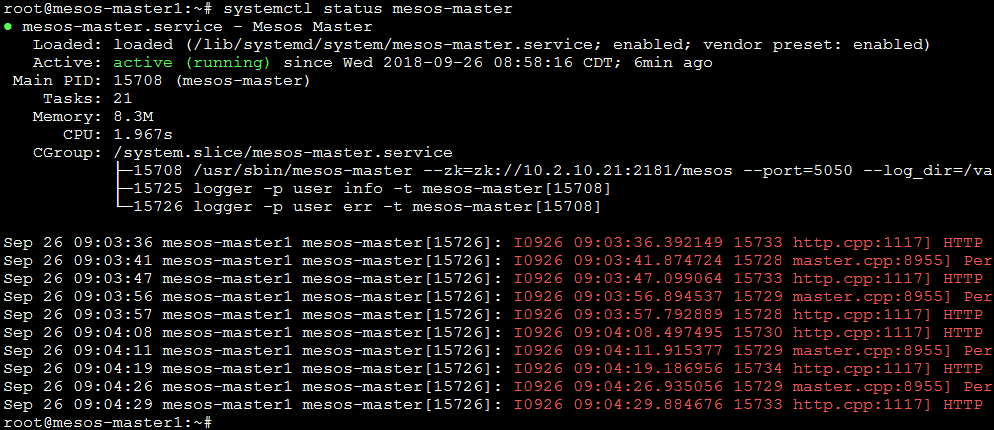
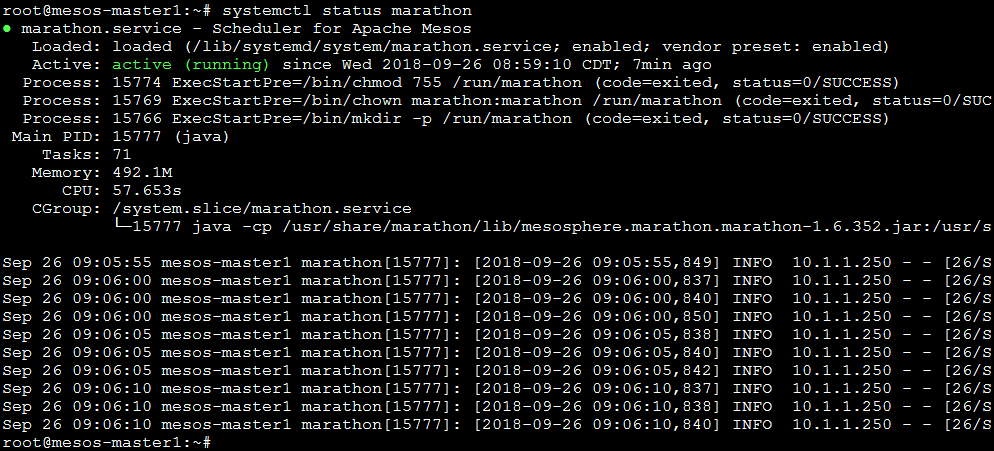
If you want to check whether the service started as expected, you can use the following commands:
systemctl status mesos-master systemctl status marathon
You should see something like the following:
Mesos:
Marathon:
For more information about the marathon service, check the about section in marathon by clicking the
?drop down in the upper right hand side of the marathon page.
If multiple
masterswere configured for high availability you can do the following to test the HA of marathon:Attention
For our lab we have only one master so this step is for documentation purposes.
- Figure out which mesos is running the framework marathon (based on our screenshot above, it is available on master1)
- Restart this master and you should see the framework was restarted automatically on another host. “mesos-master1” would change to “mesos-master2, 3, etc.”