NGINX Modern Apps > Class 10 - NMS API Connectivity Manager > Module 7 - Advanced Security Lab Source | Edit on
Step 14 - Access Control Routing with JWT Claims¶
JWT is based on OAuth and OIDC. Keycloak is the OAuth Authorization Server. Keycloak is already configured to issue JWT tokens for developers.
What is Access Control Routing?¶
In the previous labs, we configured a Policy to authorize access to /v2/colors only if a valid JWT token is presented in the request. We did two labs where we only relied on the JWT token signature (JWT validation), and a second lab where we rely on the Keycloak validation (Oauth2 introspection).
But there is no granularity and access control based on JWT claims. A claim is an attribute with a value. For instance, a claim can be added to the JWT token with the groups to which the user belongs to.
A claim looks like this:
{
"email_verified": false,
"name": "Developer Team1",
"preferred_username": "dev1",
"given_name": "Developer",
"family_name": "Team1",
"email": "dev1@f5.com",
"group": "sales"
}
Note
As you can notice, there is a claim named group and the value for dev1 user is sales
In Keycloak, we created two users with the following attributes (claims)
dev1with attributgroupand valuesalesdev2with attributgroupand valuevip
Note
We only want users part of the group vip to be allowed to ADD or REMOVE words. It means HTTP methods DELETE and POST. We will do it on the COLORS endpoint (/v2/colors)
Add Access Control Routing on API-Proxy¶
Edit
API-Proxyv2like previously (we are going toadda security policy on top of theOauth2 Introspection)Add a new
Access Control RoutingpolicyIn
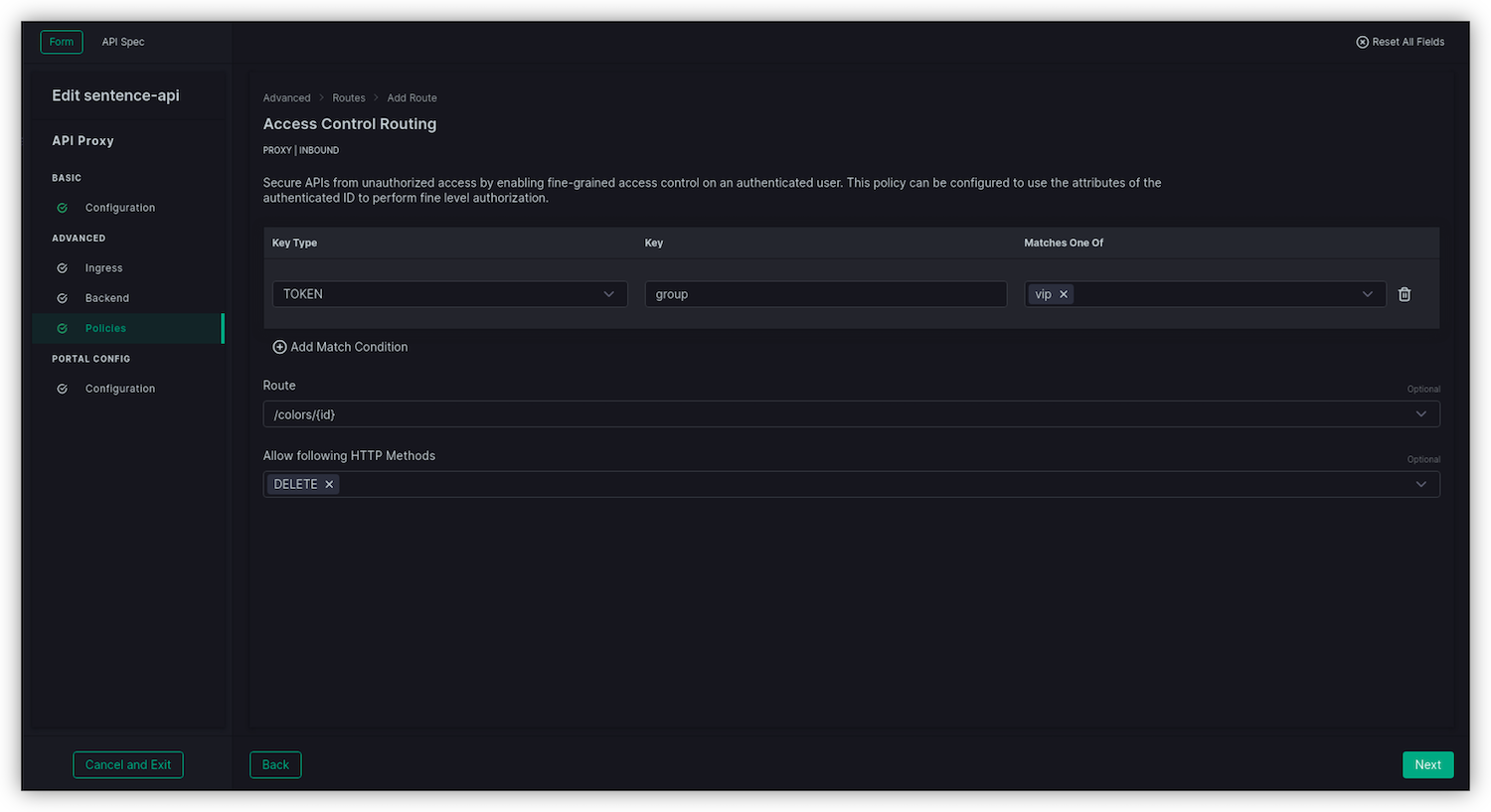
Access Control Routessection click onAdd Routeto create the first rule for /colors/{id} (the DELETE endpoint)- Key type : TOKEN
- Key : group
- Matches One of : vip
- Route : /colors/{id}
- Allow the following HTTP Methods : DELETE
- Click
Next
While still in the
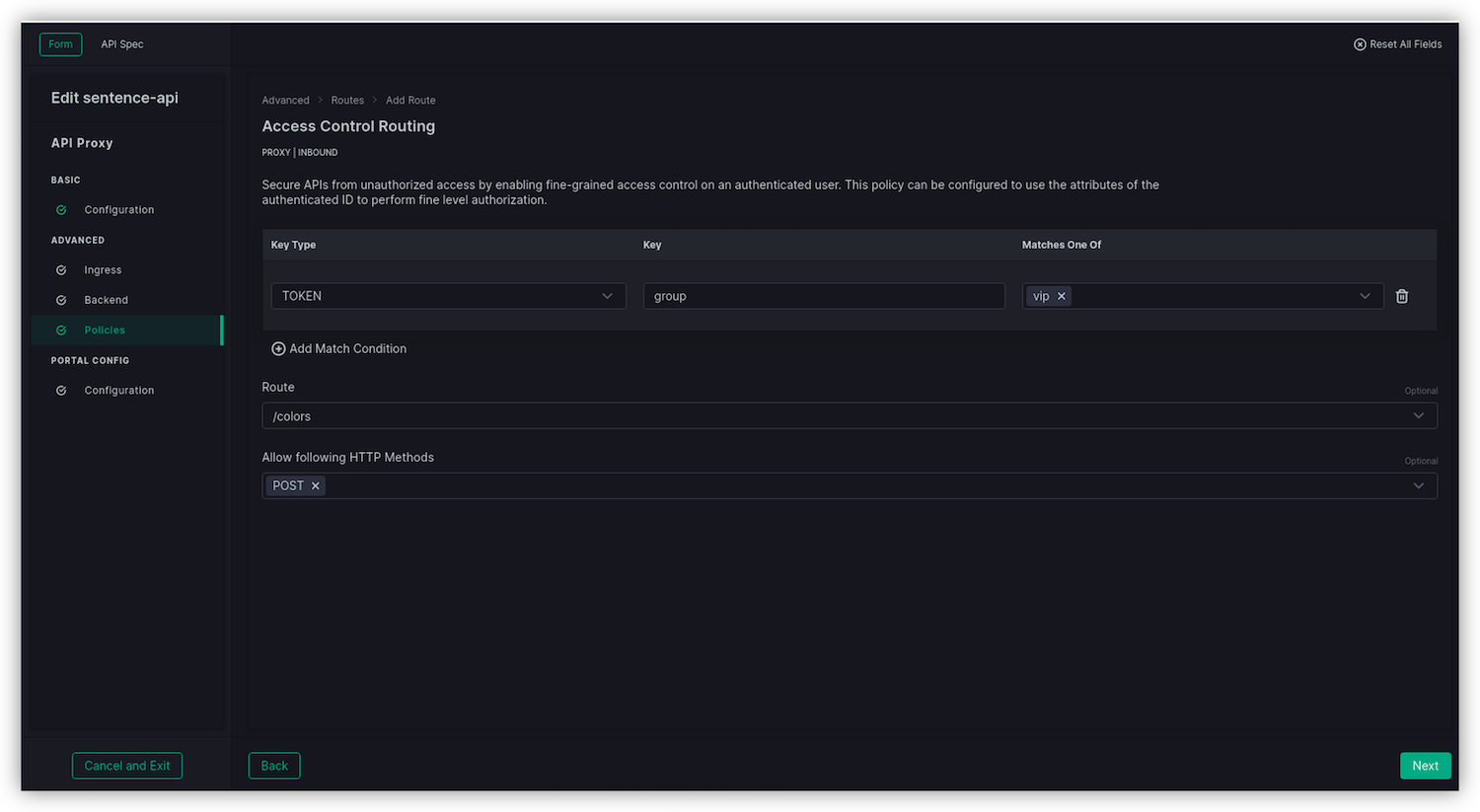
Access Control Routessection, click onAdd ACRto create the second rule for /colors (the POST endpoint)- Key type : TOKEN
- Key : group
- Matches One of : vip
- Route : /colors
- Allow the following HTTP Methods : POST
- Click
Next
Click
AddClick
Save and Publish
Test the Access Control Routing policy¶
Test with a GET¶
The GET is not part of the ACR policy; no claim will be checked.
In Postman, select the call
GET Colorsand check the version isv2http://api.sentence.com/v2/api/colorsIn Authorization, select type
OAuth 2.0Note
As you can notice, the Postman OAuth v2.0 client is already set to request JWT against Keycloak
Scroll down and click on
Get New Access Token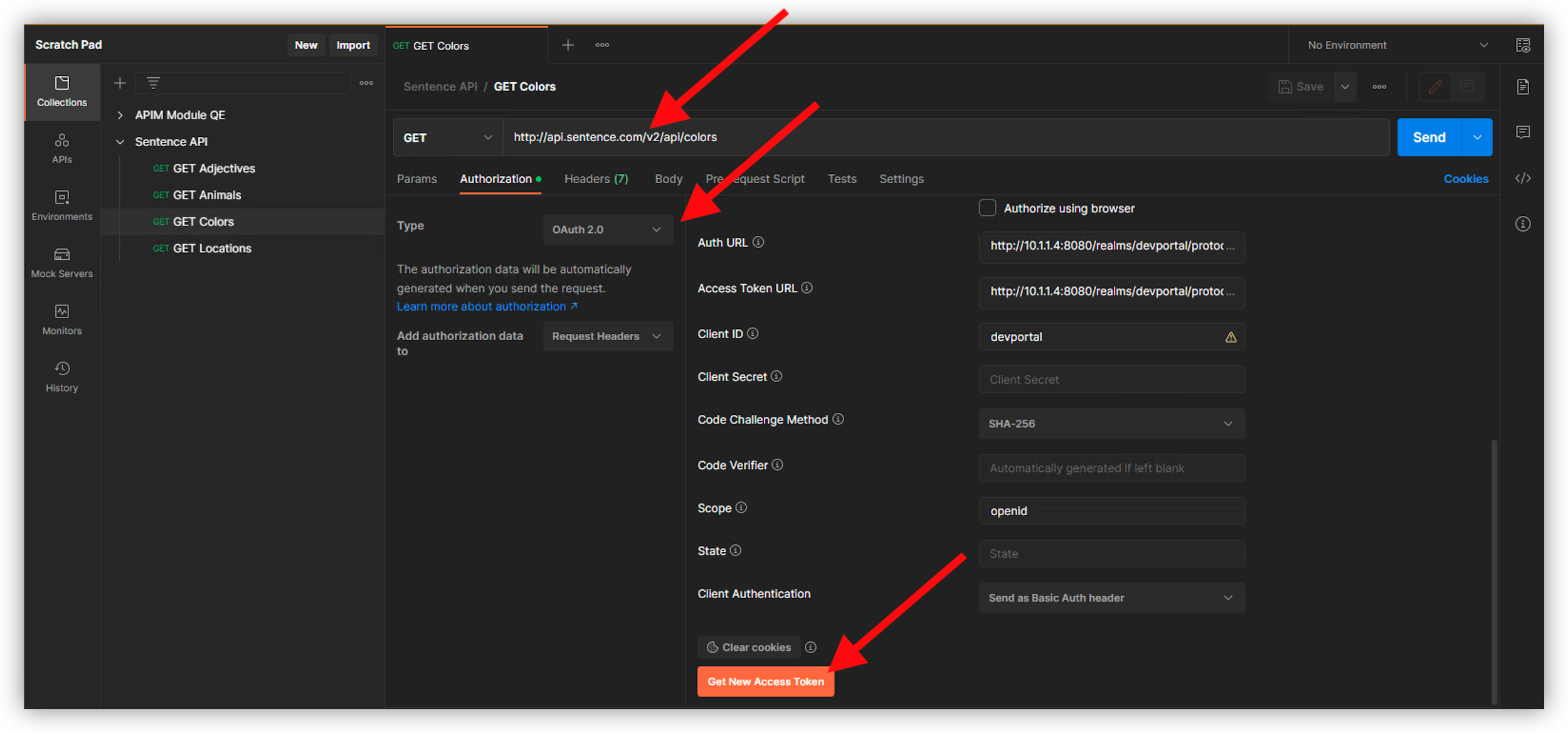
Authenticate as
dev1and passworddev1
Click
Proceed, thenUse Token
Send the request. It should pass.
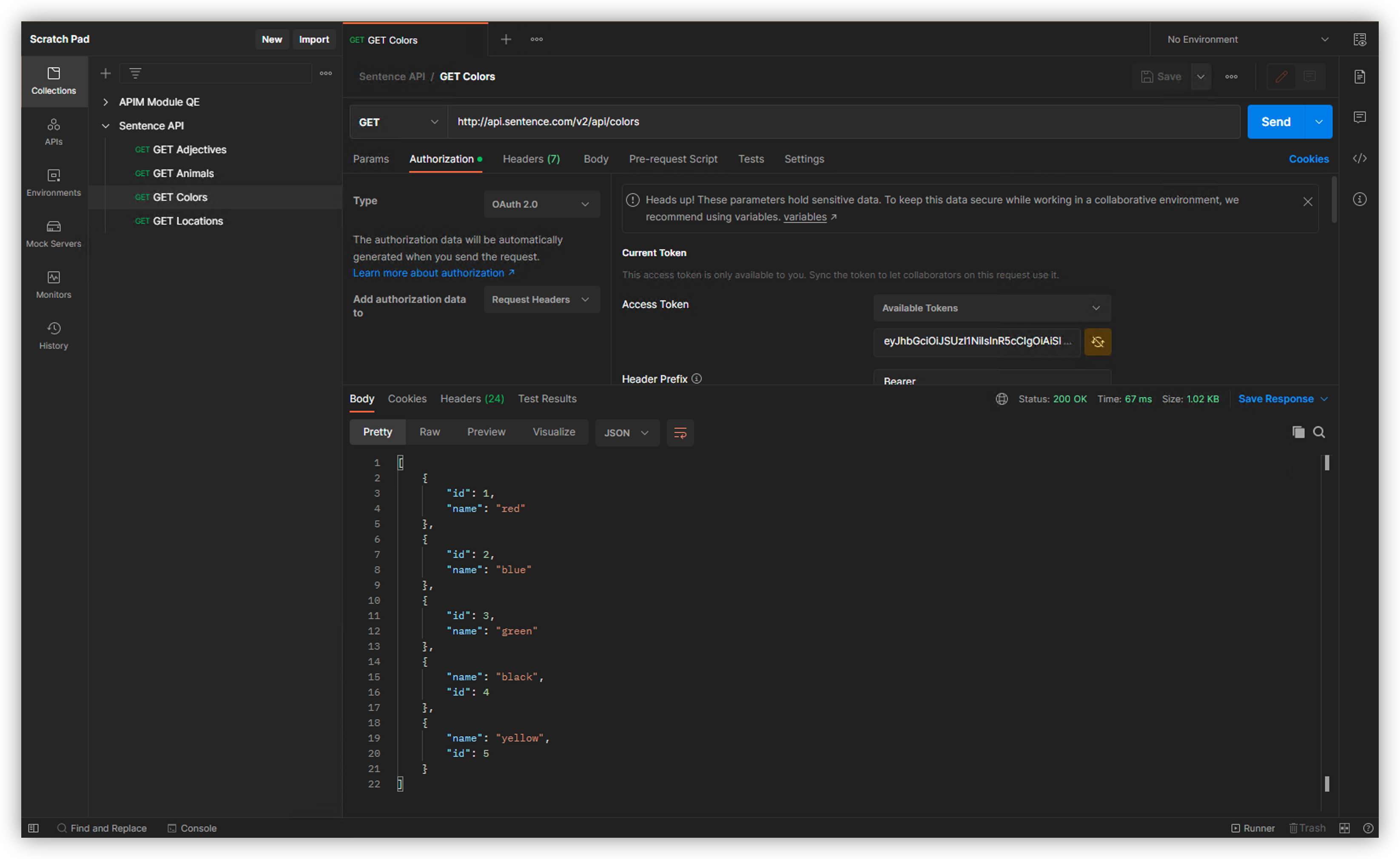
Note
You can redo the same test but with the user dev2 and password dev2. The user will be allowed to access GET /colors as the GET method has no claims control.
Test with a DELETE¶
Note
As a reminder, only users with claim group and value vip can DELETE. But the dev1 user is not in the vip group, as it is in the sales group
Below is a quick extract of dev1 and dev2 JWT tokens. You can notice the group claim is different.
{ "scope": "openid email profile", "sid": "7277008d-48e7-461a-ac9c-a6f736126e01", "email_verified": false, "name": "Developer Team1", "preferred_username": "dev1", "given_name": "Developer", "family_name": "Team1", "email": "dev1@f5.com", "group": "sales" }{ "scope": "openid email profile", "sid": "20d44034-6bb2-4817-b69a-216cc483a586", "email_verified": false, "name": "Developer Team2", "preferred_username": "dev2", "given_name": "Developer", "family_name": "Team2", "email": "dev2@f5.com", "group": "vip" }
In Postman, select the call
DELETE Colorsand check the version isv2http://api.sentence.com/v2/api/colorsIn Authorization, select type
OAuth 2.0Scroll down and click on
Get New Access Token
Authenticate as
dev1and passworddev1if you are prompted
Click
Proceed, thenUse Token
Send DELETE request to http://api.sentence.com/v2/api/colors/5 It should not pass. You can see a
403 Forbidden. Dev1 user does not belong to thevipgroup.
Clear the cookies in Postman, and request a new token but with the
dev2user. Password isdev2.
You can now DELETE entry number #5 (http://api.sentence.com/v2/api/colors/5)

Test with a POST¶
You can do the same exercise with the POST call. Only vip users are allowed (dev2)
Clear your cookies
Authenticate as
dev1, make a test POST Request to http://api.sentence.com/v2/api/colors You should see a 403 Forbidden error.Clear the cookies
Authenticate as
dev2, make a test test POST Request to http://api.sentence.com/v2/api/colors This test should complete with a status of 201 Created. The body of the API call with addyellowas an avaiable color.
Note
Congrats, you applied two Access Control Routing rules to only allow specific users to DELETE and POST entries in the API application.