NGINX Modern Apps > Class 15 - Introduction to F5 AI Gateway Source | Edit on
Module 3 - Understanding the AI Assistant application flow¶
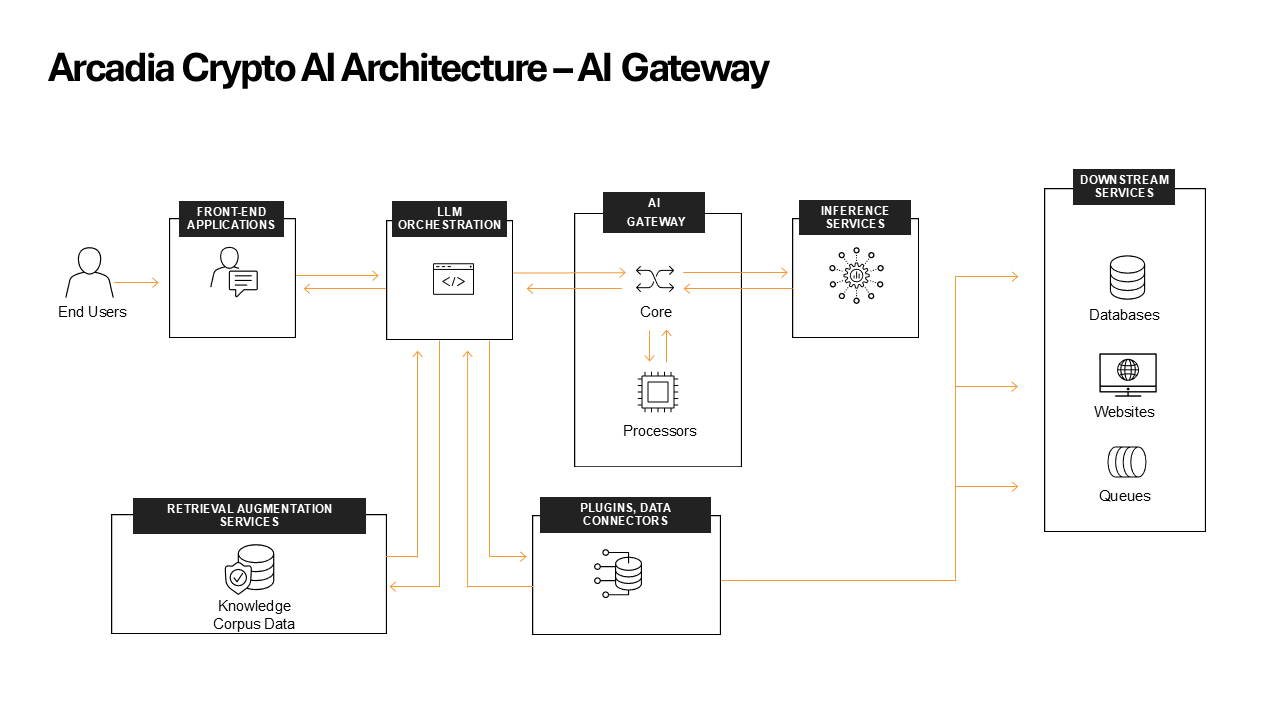
Let’s start by explaining the different functions. We will focus only on the most relevant parts of the flow.
Arcadia Crypto’s application architecture¶
Front End Application
This is the AI Assistant chatbot that you will be interacting with.
AI Orchestrator
The AI Orchestrator acts as the central hub of the entire AI system, managing the flow of information between various components. Here’s a detailed look at its functions:
- Request Handling: It receives and processes user queries, preparing them for further processing.
- LLM Interaction: The Orchestrator sends the constructed prompt to Ollama (Inference Service) and receives its responses.
- Response Formatting: It processes the LLM’s output, potentially formatting or filtering it before sending it back to the user.
- State Management: The Orchestrator maintains the state of the conversation, ensuring continuity across multiple user interactions.
- Error Handling: It manages any errors or exceptions that occur during the process, ensuring graceful failure modes.
Inference Services
Inference services will run a model in order to generation predictions. This lab uses Ollama, a popular open source solution for inference. Ollama facilitates the local execution of large language models (LLMs) such as Llama 2, Mistral, and in our case LLama 3.1 8B. The key features of Ollama:
- Local Execution: Users can run powerful language models directly on their machines, enhancing privacy and control over data.
- Model Customization: Ollama supports the creation and customization of models, allowing users to tailor them for specific applications, such as chatbots or summarization tools.
- User-Friendly Setup: The tool provides an intuitive interface for easy installation and configuration on macOS, Linux and Windows.
- Diverse Model Support: Ollama supports a variety models, making it versatile for different natural language processing tasks.
- Open Source: Ollama is an open-source platform, which means its source code is publicly available, allowing for community contributions and transparency.
The traffic is passing from the Front End Application to the AI Orchestrator where the conversation chat is maintained. The AI Orchestrator will pass the chat to Ollama through the AI Gateway which will perform the security inspection both on the request and the response.
Understanding the AI Gateway initial config¶
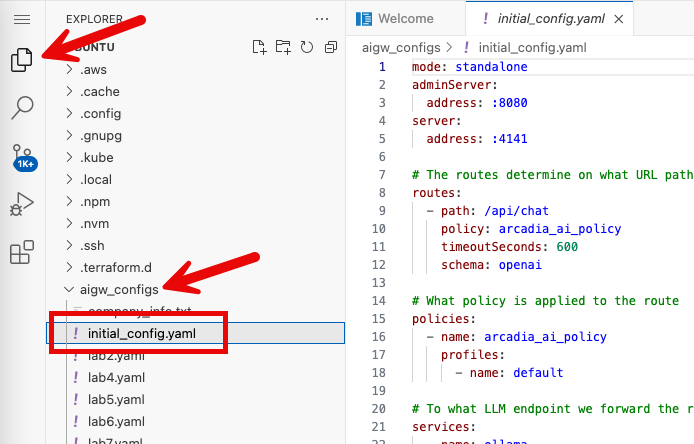
To find the initial configuration for AI Gateway, go to your VS Code tab and navigate to the Explorer, open the aigw_configs
folder and find initial_config.yaml.
First we define what is the endpoint of the inference service that hosts the LLM.
Next we need to define a profile that points to the service.
Next we define a policy and attach the profile to it.
Lastly, we combine everything with a route which is the entry point that the AI Gateway is listening on.
The final configuration will look as the following and is currently applied to the AI Gateway:
routes: - path: /api/chat policy: arcadia_ai_policy timeoutSeconds: 600 schema: openai # What policy is applied to the route policies: - name: arcadia_ai_policy profiles: - name: default # To what LLM endpoint we forward the request to services: - name: ollama executor: http config: endpoint: "http://ollama_public_ip:11434/api/chat" schema: ollama-chat # What do we do with the request, at the moment we just forward it profiles: - name: default services: - name: ollama
Interact with the AI Assistant and review the logs¶
Go ahead and ask the AI Assistant a question.
Then review the AI Gateway logs from the AI Gateway Web Shell tab you previously opened. Your previously run
command should continue to show you new log entries. You may need to scroll to the bottom of the screen in order to
see them. If you are back at the terminal prompt, run the docker logs aigw-aigw-1 -f command again to view the logs.