NGINX Modern Apps > Class 15 - Introduction to F5 AI Gateway Source | Edit on
Introduction¶
What is Generative AI?¶
Generative AI (Gen AI) is a class of artificial intelligence systems designed to generate new content, such as text, images, audio, video, and even code, based on patterns learned from existing data. Moving beyond traditional AI, which focused primarily on classification and prediction tasks, generative AI creates original output that mimics human creativity.
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?¶
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence system that is trained to understand, generate, and manipulate human language at a large scale. LLMs are built using machine learning techniques, particularly deep learning, and they are a subset of AI technologies. Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI where machines learn from data to improve their performance on specific tasks without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning is a subset of ML that uses neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) to model complex patterns in data.
Architecture - The backbone of LLMs is the transformer architecture, which uses attention mechanisms to focus on relevant parts of the input text.
Training - LLMs are trained on enormous corpora of text data (e.g., books, websites, and documents) using techniques like unsupervised learning (predicting missing words or sequences) and fine-tuning (training on specific tasks with labeled data).
Inference - Once trained, LLMs can generate predictions or responses by continuing a sequence of text based on their learned knowledge.
As AI continues to grow at a very fast rate, the need for AI in business environment is rapidly increasing. The need for helpful AI tools, like chatbots or assistants, for customers to interact with and ask questions to, has significantly increased the need for AI in business. It also presents a challenge in properly securing and observing AI traffic in todays environments.
Overview of AI Gateway¶
F5 AI Gateway is a specialized platform designed to route, protect, and manage generative AI traffic between clients and Large Language Model (LLM) backends. It addresses the unique challenges posed by AI applications, particularly their non-deterministic nature and the need for bidirectional traffic monitoring.
The main AI Gateway functions are:
Core¶
The Core performs the following tasks:
- Performs Authn/Authz checks, such as validating JWTs and inspecting request headers.
- Parses and performs basic validation on client requests.
- Applies Processors to incoming requests, which may modify or reject the request.
- Selects and routes each request to an appropriate LLM backend, transforming requests/responses to match the LLM/client schema.
- Applies Processors to the response from the LLM backend, which may modify or reject the response.
- Optionally, stores an auditable record of every request/response and the specific activity of each processor. These records can be exported to AWS S3 or S3-compatible storage.
- Generates and exports observability data via OpenTelemetry
- Prevents malicious inputs from reaching LLM backends
- Ensures safe LLM responses to clients
- Protects against sensitive information leaks
- Providing comprehensive logging of all requests and responses
Processors¶
A Processor runs separately from the core and can perform one or more of the following actions on a request or response:
- Modify: A processor may rewrite a request or response. For example, by redacting credit card numbers.
- Reject: A processor may reject a request or response, causing the core to halt processing of the given request/response.
- Annotate: A processor may add tags or metadata to a request/response, providing additional information to the administrator. The core can also select the LLM backend based on these tags.
What are the use cases for AI Gateway?¶
AIGW acts as a hub for integration and streamlining of AI applications with AI services (OpenAI, Anthropic, Mistral, Ollama, etc.). Now that we have an understanding of what AI Gateway is and how it works we will need to achieve the below architecture.
General use cases:
- Prompt injections: Detect and block any prompt injections or
jailbreaks
- Prompt management
- Prompt templates
- RBAC for LLM providers (only access certain LLMs)
- Prompt leakage: block before it gets to LLM
- Prompt-based routing
- Cost effective routing
- Best-fit model routing
- Model hallucination prevention
- Load balancing (failover, circuit breaking)
- Rate limiting
- AuthN/AuthZ
- Centrally manage credentials (such as API keys to AI services)
- PII Leakage / Data leakage: Accidental leakage of personal
information from LLM (i.e. financial, health care information)
- Email address
- Social Security Number (SSN)
- Date of birth
- Credit card numbers
- Data exfiltration
Where does AI Gateway fit in the data flow?¶
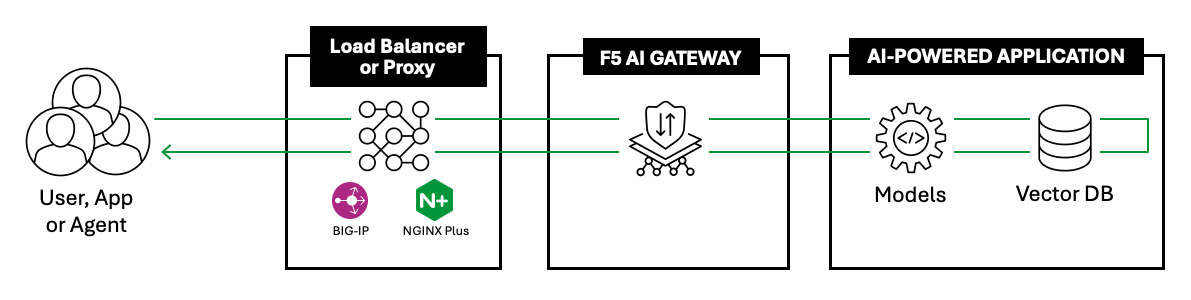 F5 AI Gateway should be architected behind a proxy (i.e. BIG-IP, NGINX). This proxy can then manage Layer 7 traffic and provide WAF protections before traffic reaches AIGW. Once traffic reaches AIGW, it is handling the AI specific traffic and focuses on analyzing the prompt and taking required action based on AIGW’s configuration.
F5 AI Gateway should be architected behind a proxy (i.e. BIG-IP, NGINX). This proxy can then manage Layer 7 traffic and provide WAF protections before traffic reaches AIGW. Once traffic reaches AIGW, it is handling the AI specific traffic and focuses on analyzing the prompt and taking required action based on AIGW’s configuration.