NGINX Modern Apps > Class 2 - NGINX Plus CI/CD Lab Source | Edit on
Module 3: Continuous Deployment for NGINX Plus Load Balancers¶
In this exercise, we will be using a CI/CD pipeline to deploy NGINX Plus Load balancer.
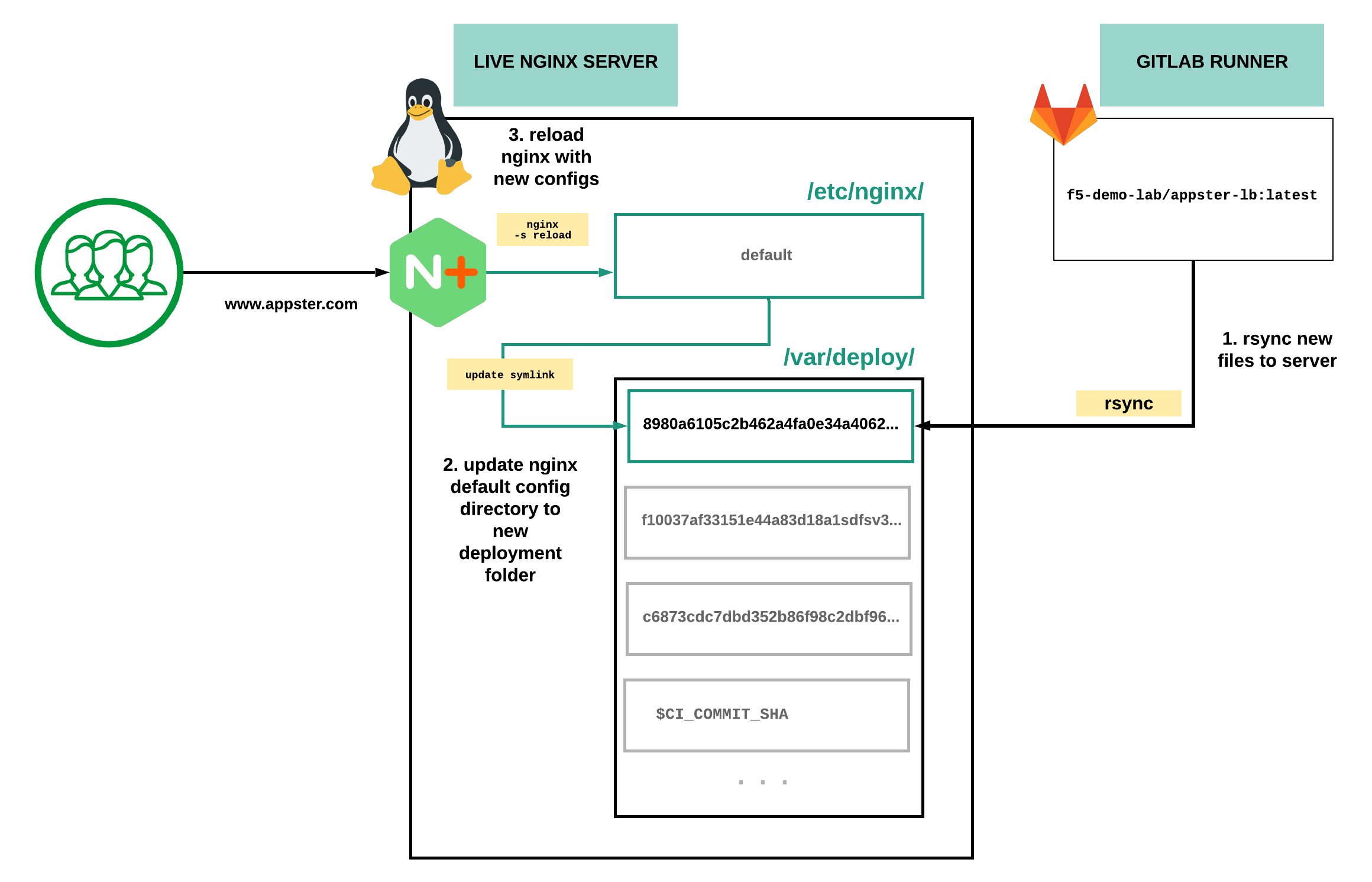
Instead of deploying NGINX Plus as a container into our live environments as we did in the previous exercise, we will be pushing new NGINX configuration into a new deployment folder, the filesystem of our NGINX Plus Virtual Machine.
Next, we create a Symbolic link to
point the default NGINX config directory, /etc/nginx to this new
deployment folder, /var/deploy/[$CI_COMMIT_SHA].
Lastly, we will reload NGINX with the new NGINX configuration gracefully without dropping connections.
The Commit SHA is a unique hash referring to a particular commit of code. Because we deploy new NGINX Plus configurations in a new folder using a Commit SHA as the folder name, we can quickly revert to known NGINX configuration consistent with the code commit in Gitlab’s git repository.
NGINX can reload a new configuration without any downtime, and without interrupting any current connections. A soft-reconfiguration spawns a new set of NGINX worker processes; the old ones continue to work until completion (but do not accept new requests - all new applications are accepted by the new set of worker processes). Live binary upgrades work similarly. If the upgrade is successful, the old set of NGINX worker processes are signaled to terminate, and the new set takes over. For more information, please see: Controlling NGINX
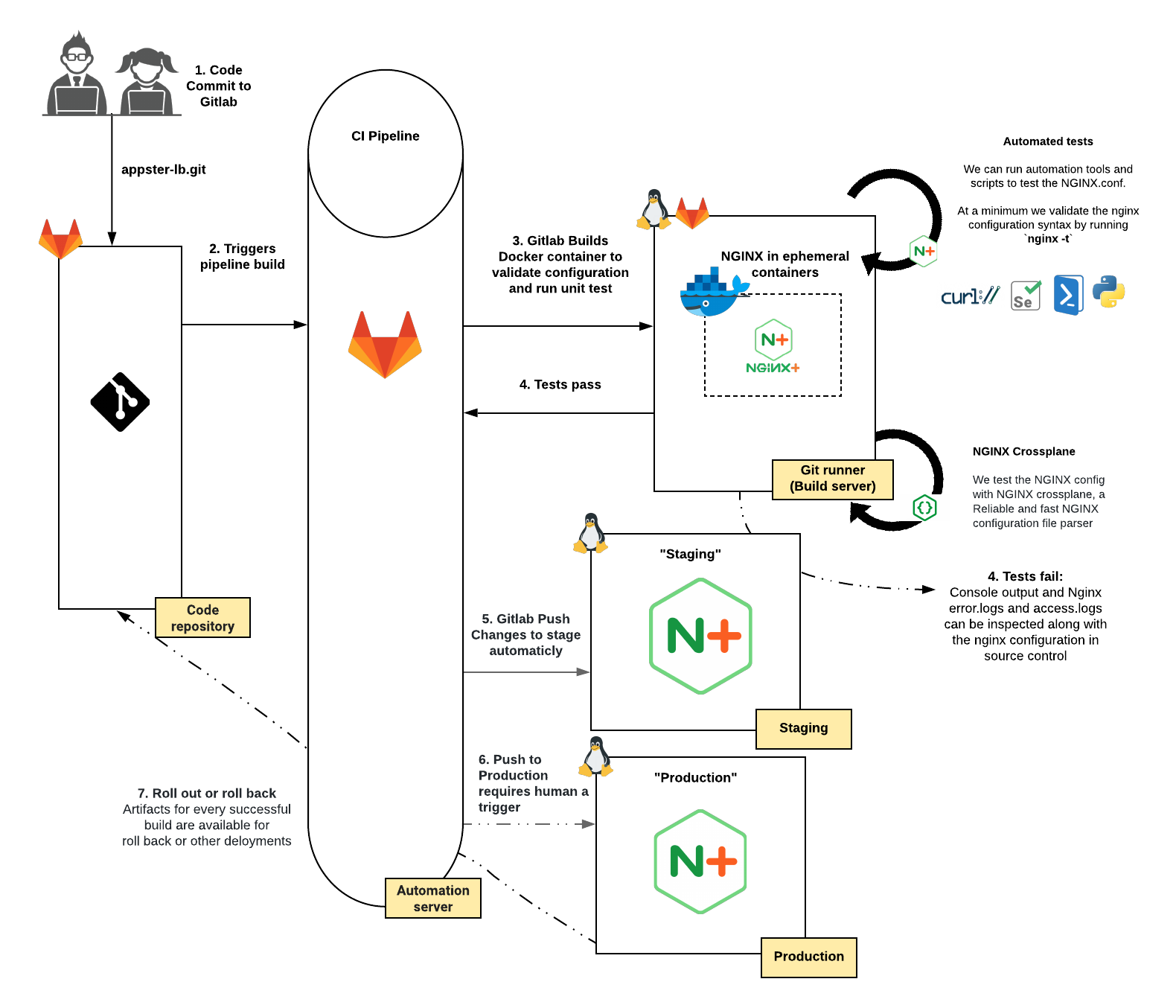
CI/CD flowchart¶
The diagrams below depicts the workflow from code to deployment.
Here is an overview of the entire CI/CD Pipeline
Here is a closer look at steps 5 and 6, where we use rsync to
deploy the new NGINX configuration files to live NGINX servers
Important
Run all lab activites from the Windows JumpHost