F5 BIG-IP SSL Orchestrator Training Lab > All SSL Orchestrator Lab Guides > SSLO 301: Automating SSL Orchestrator Deployments in Public Cloud (Agility 2022 | 2 hours) > 2. Automating BIG-IP (SSL Orchestrator) Provisioning with Terraform Source | Edit on
2.2. Lab Scenario¶
Two AWS VPCs are connected by an AWS Transit Gateway, which routes traffic between the VPCs. The Application VPC contains a Wordpress application server instance. The Security VPC contains the BIG-IP (SSL Orchestrator) VE and inspection device instances. Users will connect to a Virtual Server on the BIG-IP to access the Wordpress application.
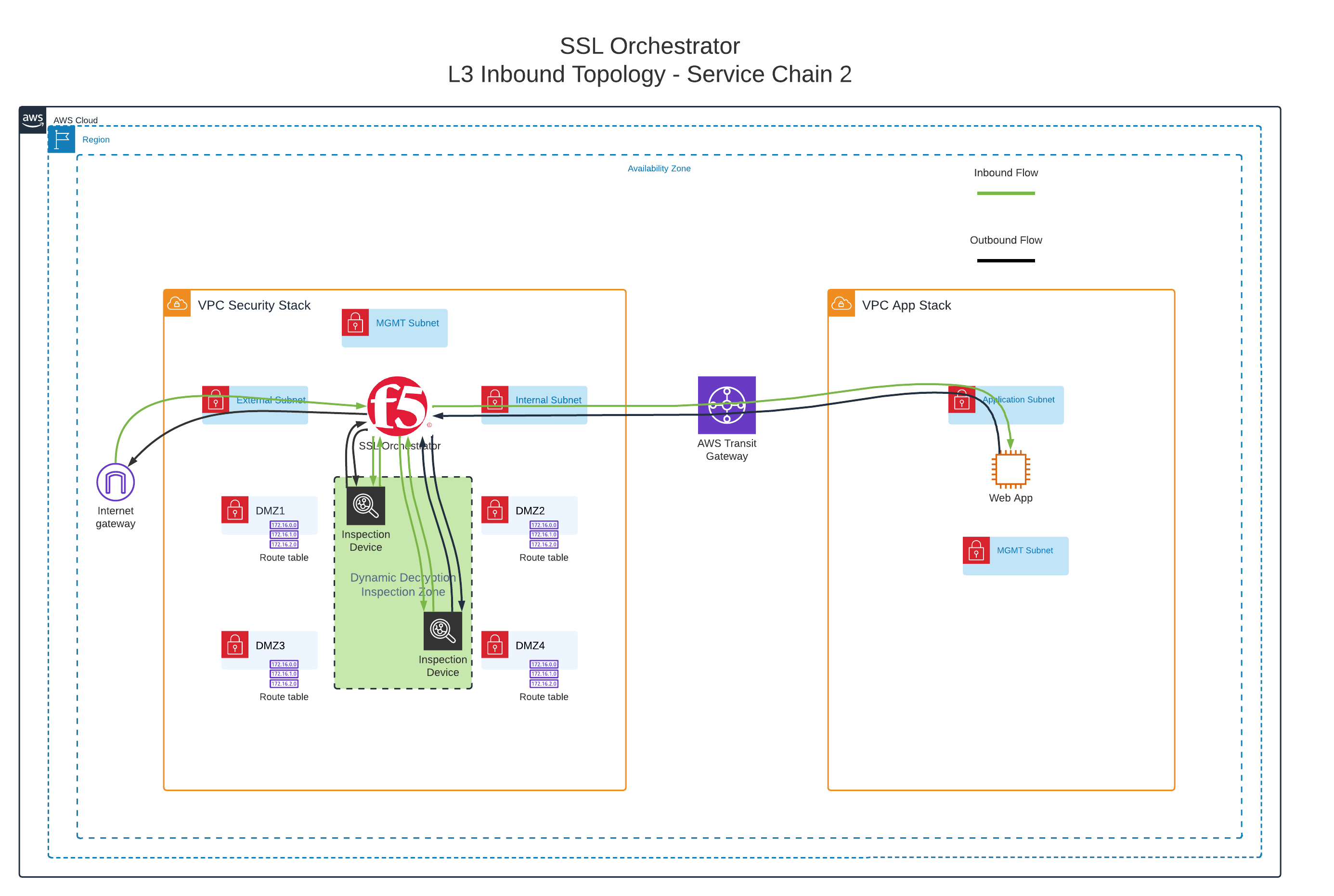
Inbound traffic will flow through one of two Service Chains before being forwarded to the application server. Two L3 inspection devices are configured. Service Chain 1 includes only the first inspection device. Service Chain 2 includes both inspection devices.
Clients connecting from the 10.0.0.0/8 CIDR range will be sent through Service Chain 1. These users are considered 'internal' clients with lower risk, so require less inspection.
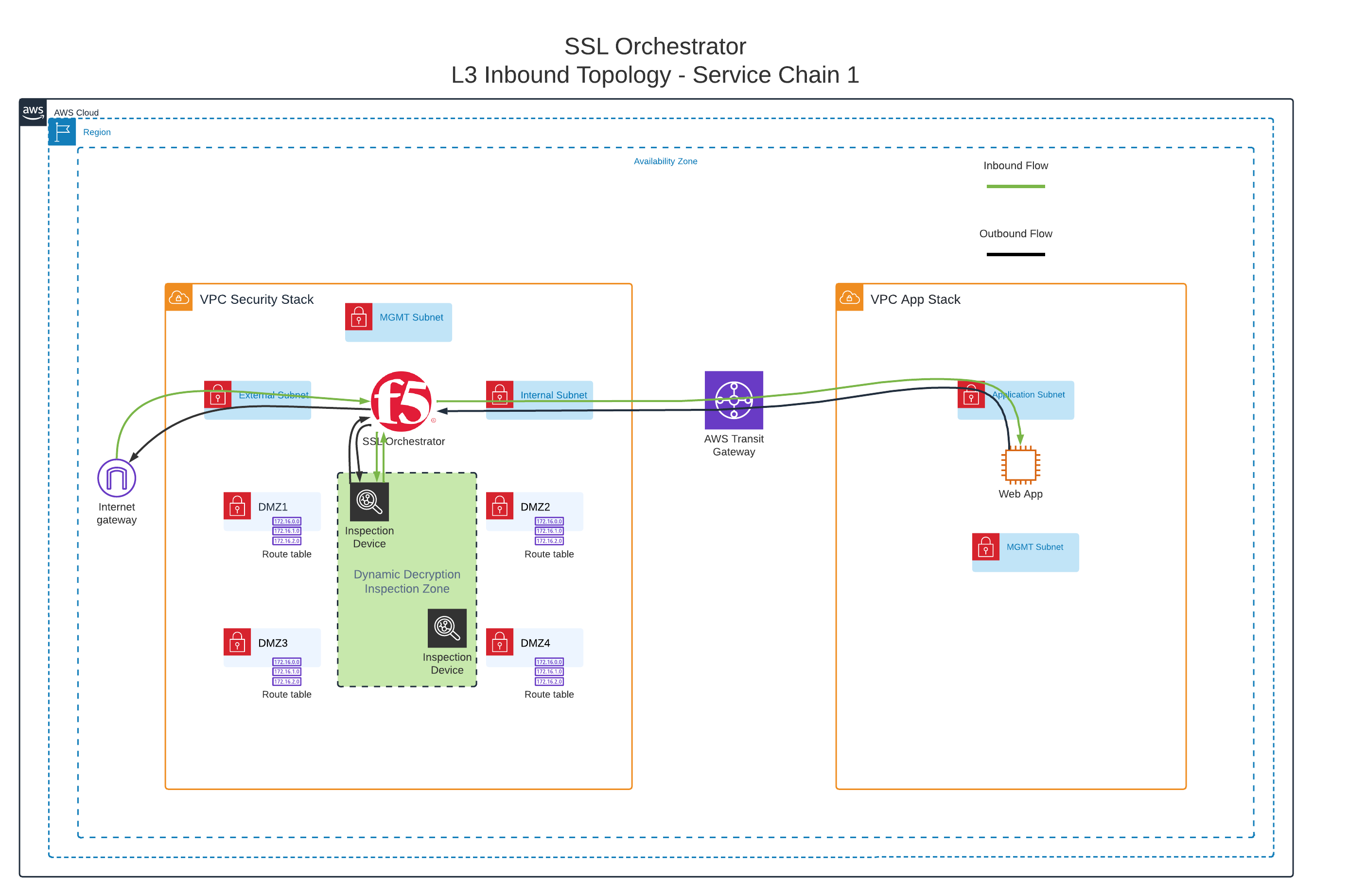
Clients from all other source networks will be sent through Service Chain 2. These users are considered 'external' (Internet) clients with higher risk, so require more inspection.
2.3. Target Infrastructure End-State¶
The Terraform configuration that you will use in this lab module deploys the following:
AWS networking resources
Wordpress application instance
Layer-3 (L3) inspection service instances
BIG-IP (F5 SSL Orchestrator) VE instance
SSL Orchestrator Network Diagram
The SSL Orchestrator interfaces are configured as follows:
Interface |
Description |
|---|---|
MGMT |
Dedicated out-of-band management interface |
1.1 |
Connected to the Internet-facing subnet |
1.2 |
Connected to the application-facing subnet |
1.3 |
Connected to L3 Inspection Service #1 - "TO Service" subnet |
1.4 |
Connected to L3 Inspection Service #1 - "FROM Service" subnet |
1.5 |
Connected to L3 Inspection Service #2 - "TO Service" subnet |
1.6 |
Connected to L3 Inspection Service #2 - "FROM Service" subnet |
Note
For this lab, the L3 inspection devices are both Snort IDS devices. However, they could be a mix of the following types: Inline L3, HTTP, ICAP, or passive tap devices.
2.3.1. Virtual Lab Infrastructure Details (and Credentials)¶
The following tables provide device/service network configuration details. Login credentials are also provided for use as directed in the lab exercises.
BIG-IP Management IP |
10.0.1.11 - Associated Public IP address is provided in Terraform outputs |
Login |
Username: admin Password: f5Twister! The root account is disabled. |
System DNS |
169.254.169.253 (AWS DNS) |
SSL Orchestrator Topology |
Name: l3inbound VS Destination: 10.0.2.200:443 SNAT: Automap Pool member: 192.168.1.200:443 Service Chain 1: SNORT1 Service Chain 2: SNORT1, SNORT2 Security Policy Rule 1: Client subnet 10.0.0.0/8 - Intercept - Service Chain 1 Security Policy Rule 2: Everything - Intercept - Service Chain 2 |
Login |
Username: user Password: user |
Login |
Username: ubuntu Password: f5Twister! |
TO Service |
Interface: 1.3 IP Address: 10.0.3.21/25 |
FROM Service |
Interface: 1.4 IP Address: 10.0.3.149/25 |
Login |
Username: ubuntu Password: f5Twister! |
TO Service |
Interface: 1.5 IP Address: 10.0.4.21/25 |
FROM Service |
Interface: 1.6 IP Address: 10.0.4.149/25 |
Warning
Simple passwords were used in this lab environment in order to make it easier for students to access the infrastructure. The jump host in this lab environment is only accessible to you after successfully authenticating to the UDF portal.
If deploying in your own lab, please follow recommended security practices of using strong passwords and restricting network access.