F5 IngressLink¶
Overview of IngressLink¶
The F5 IngressLink solution addresses modern app delivery at scale. IngressLink is a resource definition defined between BIG-IP and NGINX using F5 Container Ingress Service and NGINX Ingress Service.
F5 IngressLink is the first true integration between BIG-IP and NGINX technologies. F5 IngressLink was built to support customers with modern, container application workloads that use both BIG-IP Container Ingress Services and NGINX Ingress Controller for Kubernetes. It’s an elegant control plane solution that offers a unified method of working with both technologies from a single interface—offering the best of BIG-IP and NGINX and fostering better collaboration across NetOps and DevOps teams. The diagram below demonstrates this use case.
This architecture diagram demonstrates the IngressLink solution:
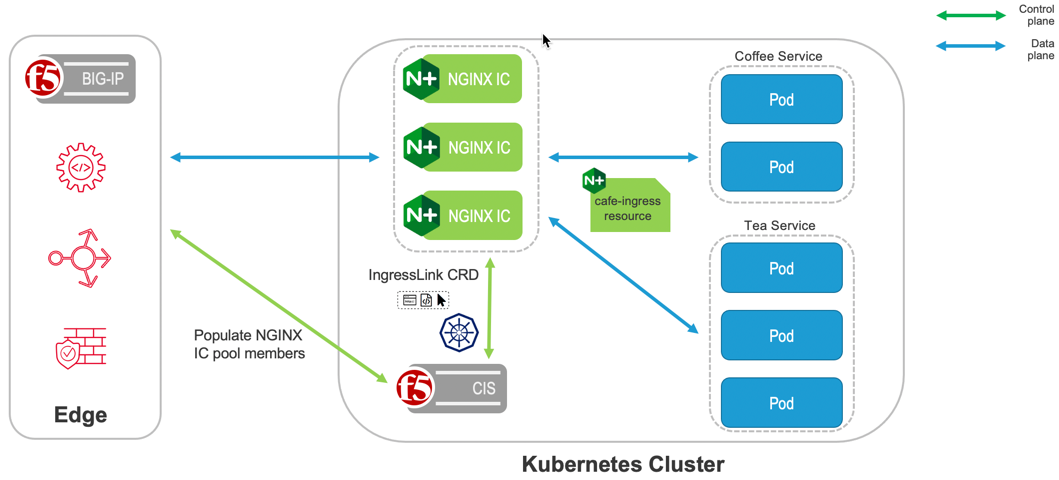
IngressLink Compatibility Matrix¶
| CIS | BIG-IP | NGINX+ IC | AS3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| v2.4+ | v13.1+ | v1.10+ | 3.18+ |
IngressLink does not have any restrictions for customizing the namespace or service endpoint. However F5 recommends using the default nginx-ingress.
Configuring IngressLink¶
Prerequisites¶
- CIS and BIG-IP are up and running
- Refer to CIS Kubernetes Installation guide or CIS Openshift Installation guide to install Container Ingress Services on Kubernetes or OpenShift.
- Make sure that you deploy CIS in CRD mode (use
--custom-resource-mode=truein your CIS Configuration).
- NGINX Ingress Controller is up and running.
- See the documentation for Installation with Manifests or Installation with Helm for more information.
- Refer to Integration with F5 BIG-IP Container Ingress Services.
- Clone the CIS repository and change to the IngressLink folder by running the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/F5Networks/k8s-bigip-ctlr.gitcd k8s-bigip-ctlr/docs/config_examples/customResource/IngressLink/
Configuration¶
Create the Proxy iRule on BIG-IP:
Log in to the BIG-IP GUI.
On the Main tab, select Local Traffic > iRules.
Select Create.
In the Name field, type a name. For example, “Proxy_Protocol_iRule”.
In the Definition field, copy the following code and then select Finished.
when SERVER_CONNECTED { TCP::respond "PROXY TCP[IP::version] [IP::client_addr] [clientside {IP::local_addr}] [TCP::client_port] [clientside {TCP::local_port}]\r\n" }In the Definition field, copy the definition from the “Proxy_Protocol_iRule” file and then select Finished.
Create CIS IngressLink Custom Resource Definition Schema by running the following command:
kubectl apply -f ingresslink-customresourcedefinition.yamlYou can leverage the IngressLink solution.
Deploy your test application:
Deploy the App:
kubectl apply -f ingress-example/cafe-secret.yamlkubectl apply -f cafe.yamlDeploy the Ingress Service:
kubectl apply -f ingress-example/cafe-ingress.yaml
Create an IngressLink Resource:
Update the
virtualServerAddressparameter in the ingresslink.yaml resource. This IP address will be used to configure the BIG-IP device. It will be used to accept traffic and load balance it among the NGINX Ingress Controller pods.kubectl apply -f ingresslink.yaml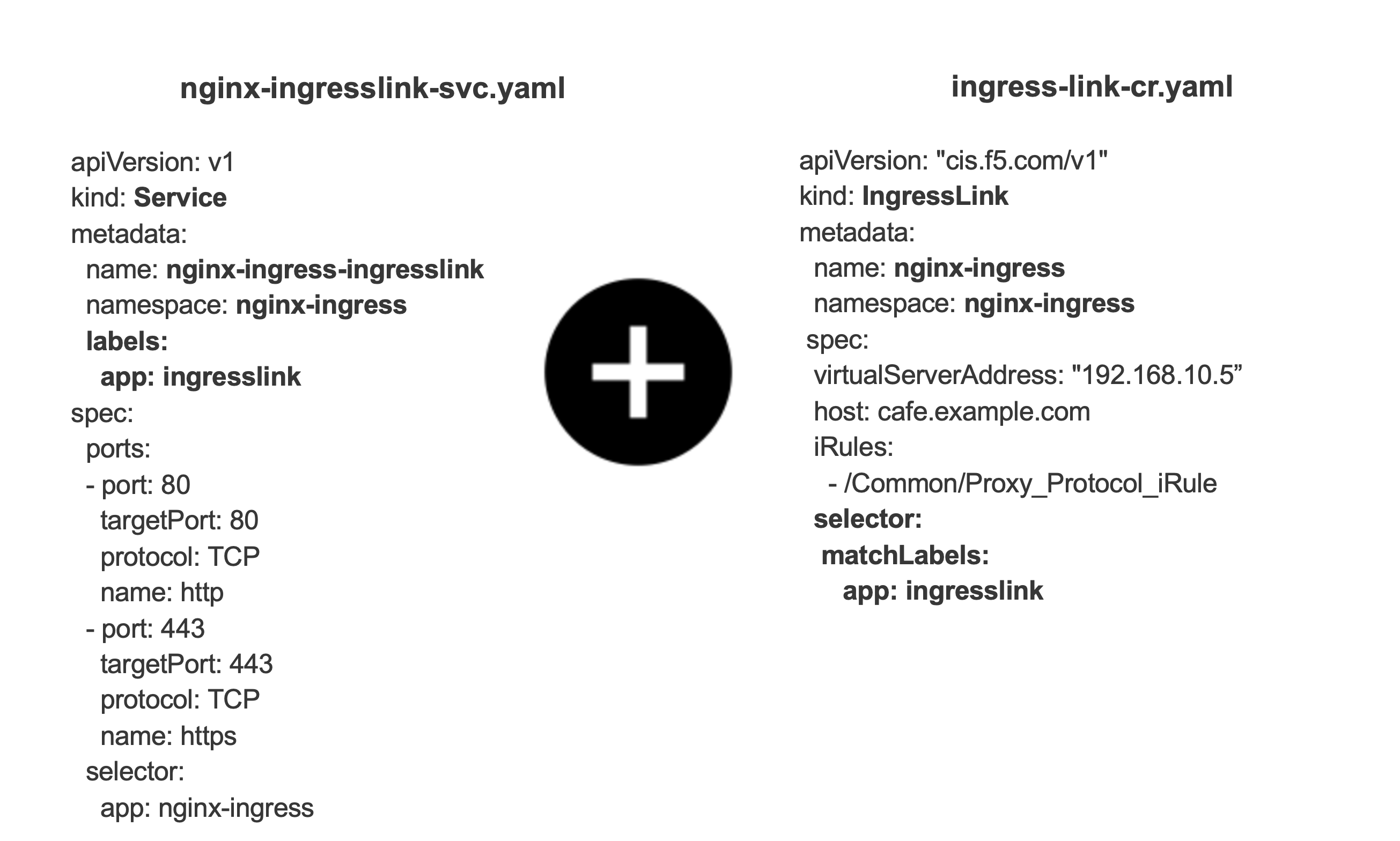
Note
- The name of the IngressLink resource should be the same which is defined during NGINX Ingress Controller installation.
- The selector in the IngressLink resource is the same as the Service labels configured in nginx-ingress-ingresslink service during NGINX Ingress Controller installation.
- The IngressLink must belong to the same namespace as the Ingress Controller pod
- nginx-ingressor the namespace used for installing the Helm chart.
Monitoring NGINX+ Ingress Controller Readiness (Optional).
You can configure the NGINX+ Ingress Controller Readiness in the nginx-ingress-ingresslink service by exposing port 8081, which is used by BIGIP to monitor NGINX+ Ingress Controller’s readiness.
nginx-ingresslink-svc.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-ingress-ingresslink namespace: nginx-ingress labels: app: ingresslink spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 80 protocol: TCP name: http - port: 443 targetPort: 443 protocol: TCP name: https - port: 8081 targetPort: 8081 protocol: TCP name: readinessport selector: app: nginx-ingress
Access the Application:
The Ingress Controller pods are behind the IP configured in Step 4 (
virtualServerAddressparameter). Test the traffic (in this example we used 192.168.10.5 as our VirtualServerAddress) by running the following command:$ curl --resolve cafe.example.com:443:192.168.10.5 https://cafe.example.com:443/coffee --insecure Server address: 10.12.0.18:80 Server name: coffee-7586895968-r26zns
Configuration Parameters¶
| Parameter | Type | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ipamLabel | String | Optional | N/A | FIC allocates IP addresses from an IPAM system’s address pool. |
| virtualServerAddress | String | Yes | N/A | IPAddress of Virtual server. |
| host | String | Optional | N/A | hostname where the application is hosted i.e. cafe.example.com. |
| iRules | List | Yes | N/A | List of iRules which needs to be attached to virtual server. |
| partition | String | Optional | N/A | BIG-IP Partition. |
You can use IPAM controller to configure and manage virtual server addresses in IngressLink by using ipamLabel. If you are using IPAM, virtualServerAddress is not required.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | apiVersion: "cis.f5.com/v1" kind: IngressLink metadata: name: nginx-ingress namespace: nginx-ingress spec: ipamLabel: "Dev". # `ipamLabel` option allows the user manage the virtual server address using the F5 IPAM controller. iRules: - /Common/Proxy_Protocol_iRule selector: matchLabels: app: ingresslink |
MultiPartition Support using Ingress Annotation¶
CRD now supports the MultiPartition feature for ingressLink CR, where the user can provision BIG-IP in multiple partitions. This helps to easily manage the bigipConfig among the partitions. The MultiPartition feature also helps to improve performance, as CIS processes only the partition when there is a change, instead of sending a unified AS3 declaration to all of the partitions on the BIG-IP every time a change/event is detected.
CIS processes multiple tenant information and still sends the single unified declaration to BIG-IP to avoid multiple posts to BIG-IP for the first time.
Note
The AS3 post call is formed as mgmt/shared/appsvcs/declare/tenant1,tenant2.
Multiple VirtualServers do not share the same virtual server address across multiple partitions. F5 does not currently support VS sharing the same host group or host with the same address in multiple partitions. The following rules apply for all VS resources. - Virtual servers with the same host group should be in one partition. - Virtual servers with the same host should be in one partition. - Virtual servers with the same VS address should be in one partition. - Virtual servers cannot share the same VIP across multiple partitions, irrespective of port.
This feature is enabled by using ingress annotation virtual-server.f5.com/partition.
Example of IngressLink using partition spec parameter: (https://github.com/F5Networks/k8s-bigip-ctlr/tree/2.x-master/docs/config_examples/customResource/IngressLink/partition)¶
FAQ¶
Q: Is Ingress Address updated with the Ingress-Link implementation?
A: No, CIS does not update the ingress address in ingress status.
Note
To provide feedback on Container Ingress Services or this documentation, please file a GitHub Issue.