Automation, Orchestration & DevOps > Class 9: Basic BIG-IP Configuration Management with Ansible > Section 1 - Ansible F5 Basic Exercises Source | Edit on
Exercise 1.3: Adding a load balancing pool¶
Objective¶
Demonstrate use of the BIG-IP pool module to configure a load balancing pool in BIG-IP device. A load balancing pool is a logical set of devices, such as web servers, that you group together to receive and process traffic.
Guide¶
Step 1:¶
Use VS Code Explorer to create a new file called bigip-pool.yml.
The Ansible node is equiped withVisual Studio Codeand can be accessed via UDF ACCESS Methods.
Step 2:¶
Enter the following play definition into bigip-pool.yml:
---
- name: BIG-IP SETUP
hosts: lb
connection: local
gather_facts: false
- The
---at the top of the file indicates that this is a YAML file. - The
hosts: lb, indicates the play is run only on the lb group. Technically there only one F5 device but if there were multiple they would be configured simultaneously. connection: localtells the Playbook to run locally (rather than SSHing to itself)gather_facts: falsedisables facts gathering. We are not using any fact variables for this playbook.
Do not exit the editor yet.
Step 3¶
Next, append the first task to above playbook. This task will use
the bigip_pool module configure the two RHEL web servers as nodes on
the BIG-IP F5 load balancer.
tasks:
- name: CREATE POOL
bigip_pool:
provider:
server: "{{private_ip}}"
user: "{{ansible_user}}"
password: "{{ansible_ssh_pass}}"
server_port: 8443
validate_certs: no
name: "http_pool"
lb_method: "round-robin"
monitors: "/Common/http"
monitor_type: "and_list"
name: CREATE POOLis a user defined description that will display in the terminal output.bigip_pool:tells the task which module to use.- The
server: "{{private_ip}}"parameter tells the module to connect to the F5 BIG-IP IP address, which is stored as a variableprivate_ipin inventory - The
provider:parameter is a group of connection details for the BIG-IP. - The
user: "{{ansible_user}}"parameter tells the module the username to login to the F5 BIG-IP device with - The
password: "{{ansible_ssh_pass}}"parameter tells the module the password to login to the F5 BIG-IP device with - The
server_port: 8443parameter tells the module the port to connect to the F5 BIG-IP device with - The
name: "http_pool"parameter tells the module to create a pool named http_pool - The
lb_method: "round-robin"parameter tells the module the load balancing method will be round-robin. A full list of methods can be found on the documentation page for bigip_pool. - The
monitors: "/Common/http"parameter tells the module the that the http_pool will only look at http traffic. - The
monitor_type: "and_list"ensures that all monitors are checked. - The
validate_certs: "no"parameter tells the module to not validate SSL certificates. This is just used for demonstration purposes since this is a lab.
Save the file and exit out of editor
Step 4¶
Run the playbook - exit back into the command line of the control host and execute the following:
[centos@ansible ~]$ ansible-playbook bigip-pool.yml
Playbook Output¶
The output will look as follows.
[centos@ansible ~]$ ansible-playbook bigip-pool.yml
PLAY [BIG-IP SETUP] ************************************************************
TASK [CREATE POOL] *************************************************************
changed: [f5]
PLAY RECAP *********************************************************************
f5 : ok=1 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
Solution¶
The finished Ansible Playbook is provided here for an Answer key. Click
here: bigip-pool.yml.
Verifying the Solution¶
Login to the F5 with your web browser to see what was configured. Grab the IP information for the F5 load balancer from the lab_inventory/hosts file, and type it in like so: https://X.X.X.X:8443/
Login information for the BIG-IP: - username: admin - password: provided by instructor, defaults to f5ansible
The load balancer pool can be found by navigating the menu on the left.
Click on Local Traffic-> then click on Pools. 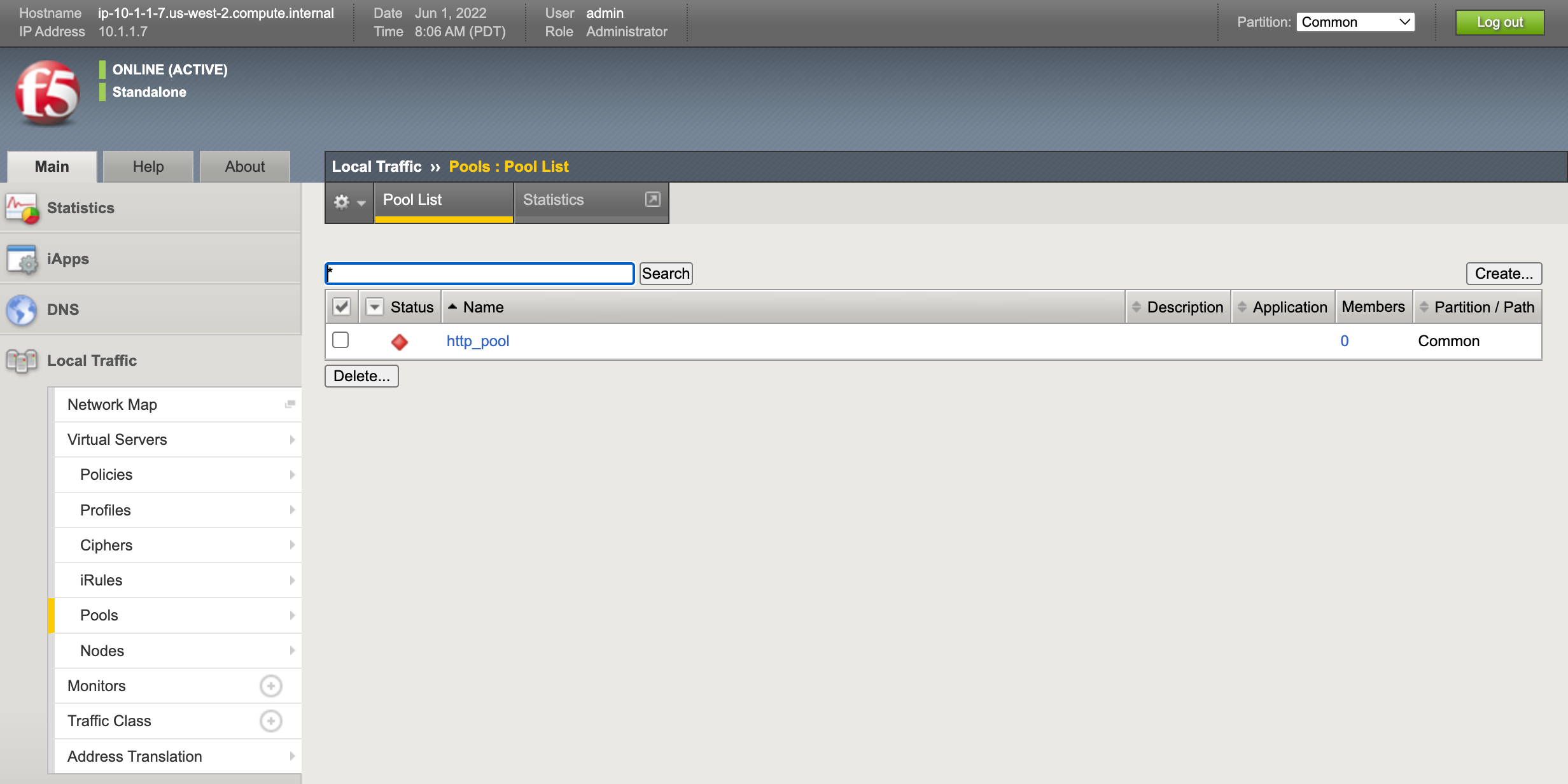
You have finished this exercise. Click here to return to the lab guide