OpenShift 4.15 and F5 BIG-IP Container Ingress Services (CIS) User-Guide for Standalone BIG-IP using OVN-Kubernetes iCNI with NO Tunnels¶
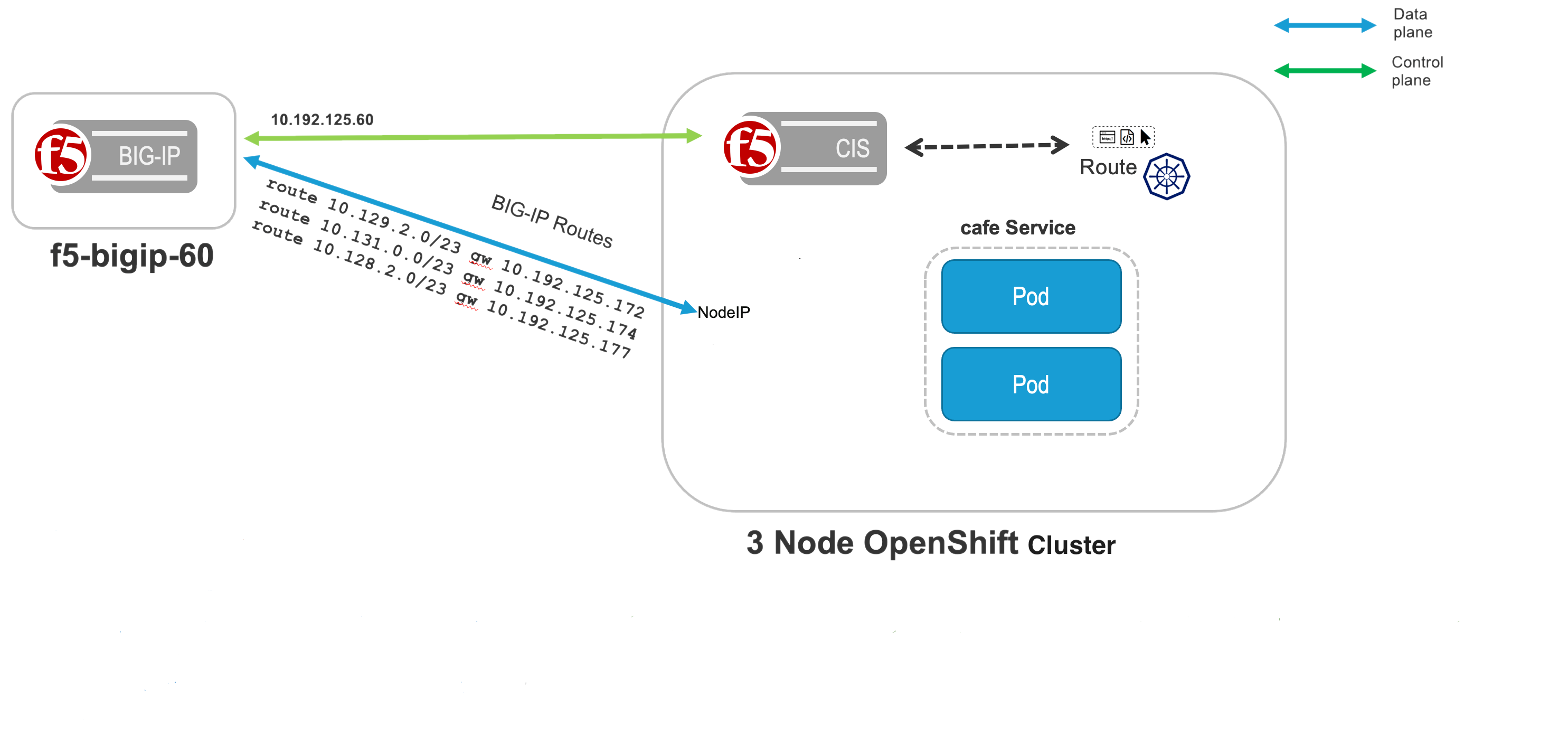
This document demonstrates how to use OVN-Kubernetes with F5 BIG-IP Routes to Ingress traffic without using an Overlay. Using OVN-Kubernetes with F5 BIG-IP Routes removes the complexity of creating VXLAN tunnels or using Calico. This document demonstrates Standalone BIG-IP working with OVN-Kubernetes. The diagram below demonstrates an OpenShift Cluster with three master, and three worker nodes. Three applications: tea, coffee and mocha are deployed in the cafe namespace.
Configuration Steps¶
Note
The configuration below has been validated on OCP versions 4.11 to 4.15.
Step 1: Deploy OpenShift using OVNKubernetes¶
Deploy the OpenShift Cluster with networkType set to OVNKubernetes. Change the default to OVNKubernetes in the install-config.yaml before creating the cluster. From OpenShift 4.12, by default networkType is OVNKubernetes.
Step 2: Deploy extended ConfigMap¶
Using extended ConfigMap
- Extended ConfigMap provides control to the admin to create and maintain the resource configuration centrally.
- namespace: cafe, vserverAddr: 10.192.125.65
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: extended-cm
namespace: kube-system
labels:
f5nr: "true"
data:
extendedSpec: |
extendedRouteSpec:
- namespace: cafe
vserverAddr: 10.192.125.65
vserverName: cafe
allowOverride: true
Deploy extended ConfigMap
oc create -f global-cm.yaml
Step-3(Optional): Configure egress from OpenShift cluster to BIG-IP(needed when no SNAT is used)¶
For OpenShift 4.12.0 to 4.14.18 versions, use the annotation
routing-external-gws(Preview Feature).Configure egress from OpenShift cluster to BIG-IP using k8s.ovn.org/routing-external-gws annotation on namespace where the application is deployed, see the figure above. Use the BIG-IP floating self-IP address for the routing-external-gws: 10.192.125.62.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
annotations:
k8s.ovn.org/routing-external-gws: 10.192.125.62 ##BIG-IP floating self-interface address rotatable to the OpenShift nodes
labels:
kubernetes.io/metadata.name: default
name: cafe
For OpenShift 4.14.19 and above versions, use the resource
AdminPolicyBasedExternalRoute(General Availability feature).Follow the instructions in Configure an external gateway on the default network.
Note
We recommend not to use this feature with versions prior to 4.14.19 due to OpenShift OVN bug (OCPBUGS-29342) prior to version 4.14.19. Pods that are created after applying
AdminPolicyBasedExternalRoutedo not have their default route changed.
Step 4: Deploy CIS¶
F5 BIG-IP Controller Ingress Services (CIS) is called the Next Generation Route Controller. The Next Generation Route Controller extended F5 CIS to use multiple Virtual IP addresses. Previously, F5 BIG-IP CIS could only manage one Virtual IP address per CIS instance.
Add the following parameters to the CIS deployment:
- Routegroup specific config for each namespace is provided as part of extendedSpec through ConfigMap.
- ConfigMap info is passed to CIS with the argument
--extended-spec-configmap="namespace/configmap-name" - Controller mode should be set to openshift enabling multiple VIP support
--controller-mode="openshift" - Configure
--static-routing-mode=trueto enable static routes on BIG-IP so that traffic can be directly route to pods. Option configurable from CIS 2.13 and above. - Configure
-orchestration-cni=ovn-k8sto configure CIS with ovn-kubernetes CNI. Option configurable from CIS 2.13 and above. - When configuring the CIS, it is necessary to define the route-label. This label is used by the CIS to filter route resources and only process those that match.
See also
The k8s-bigip-ctlr documentation for information about all config options https://clouddocs.f5.com/containers/latest/userguide/config-parameters.html
args: [
"--bigip-username=$(BIGIP_USERNAME)",
"--bigip-password=$(BIGIP_PASSWORD)",
"--bigip-url=10.192.125.60",
"--bigip-partition=OpenShift",
"--namespace=cafe",
"--pool-member-type=cluster",
"--insecure=true",
"--route-label=f5type",
"--extended-spec-configmap=kube-system/extended-cm",
"--controller-mode=openshift",
"--static-routing-mode=true",
"--orchestration-cni=ovn-k8s",
"--as3-validation=true",
"--log-as3-response=true",
]
Deploy CIS in OpenShift
oc create secret generic bigip-login -n kube-system --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=<secret>
oc create -f bigip-ctlr-clusterrole.yaml
oc create -f f5-bigip-ctlr-deployment.yaml
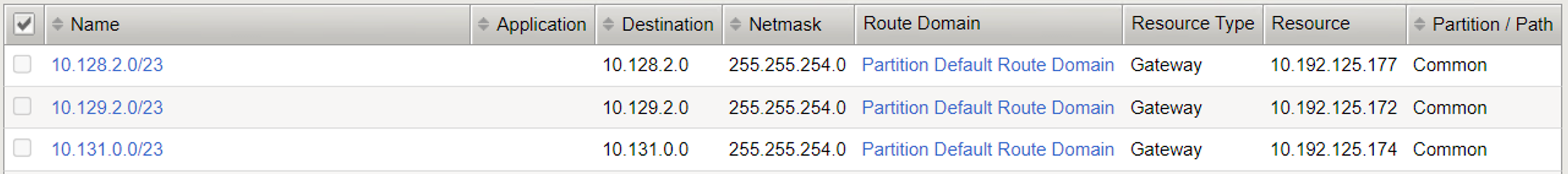
Step 5: Verify BIG-IP Static Routes¶
CIS provisions static routes on BIG-IP using the deployment parameter. For example --static-routing-mode=true
View static routes created on BIG-IP with node subnets assigned for the three worker nodes in the OpenShift cluster.
The below image captures various static routes created on BIG-IP with CIS configuration --static-routing-mode=true and --shared-static-routes=true.
Setup complete! Deploy CIS and create OpenShift Routes
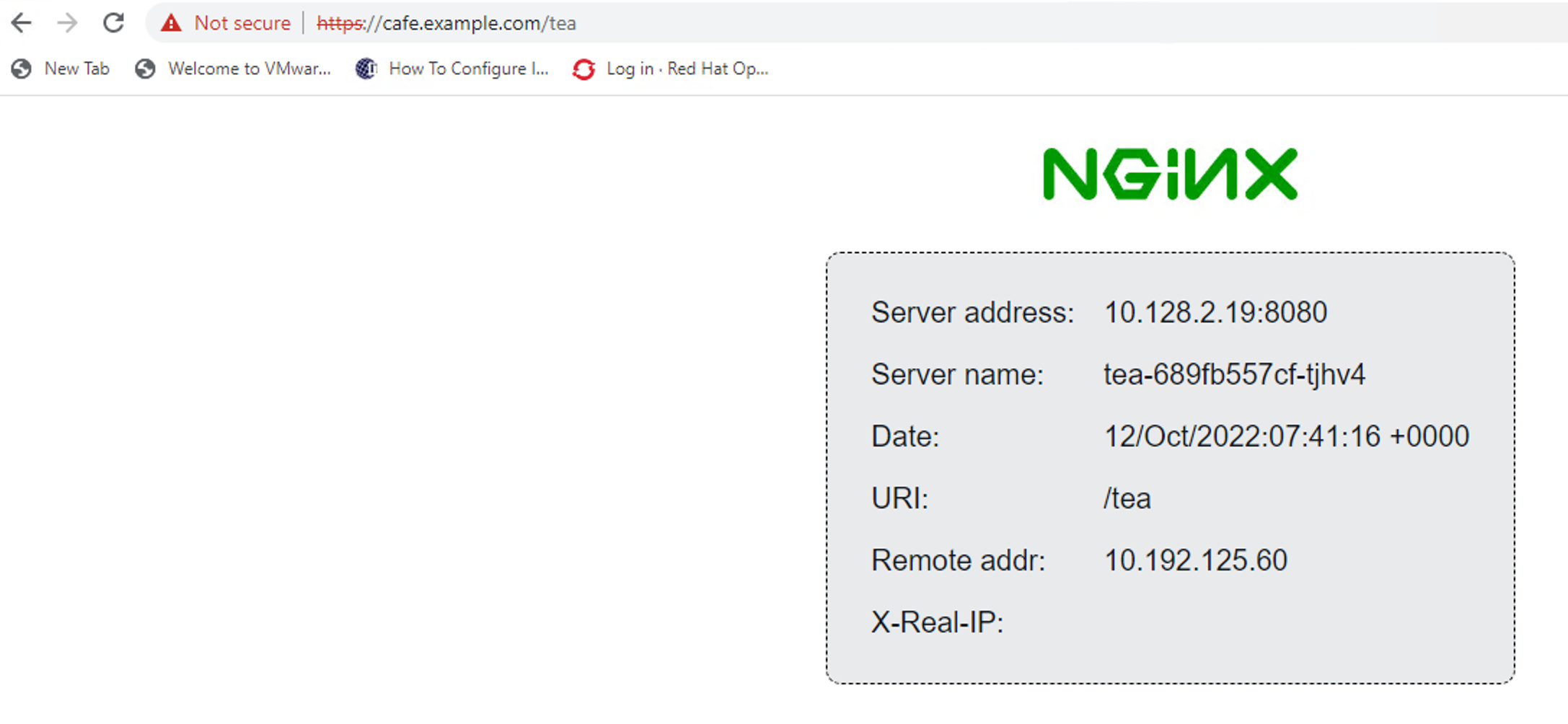
Step 6: Creating OpenShift Routes for cafe.example.com¶
User-case for the OpenShift Routes:
- Edge Termination
- Backend listening on PORT 8080
Create OpenShift Routes:
oc create -f route-tea-edge.yaml
oc create -f route-coffee-edge.yaml
oc create -f route-mocha-edge.yaml
Validation¶
Step 1: Validate OpenShift Routes using the BIG-IP¶

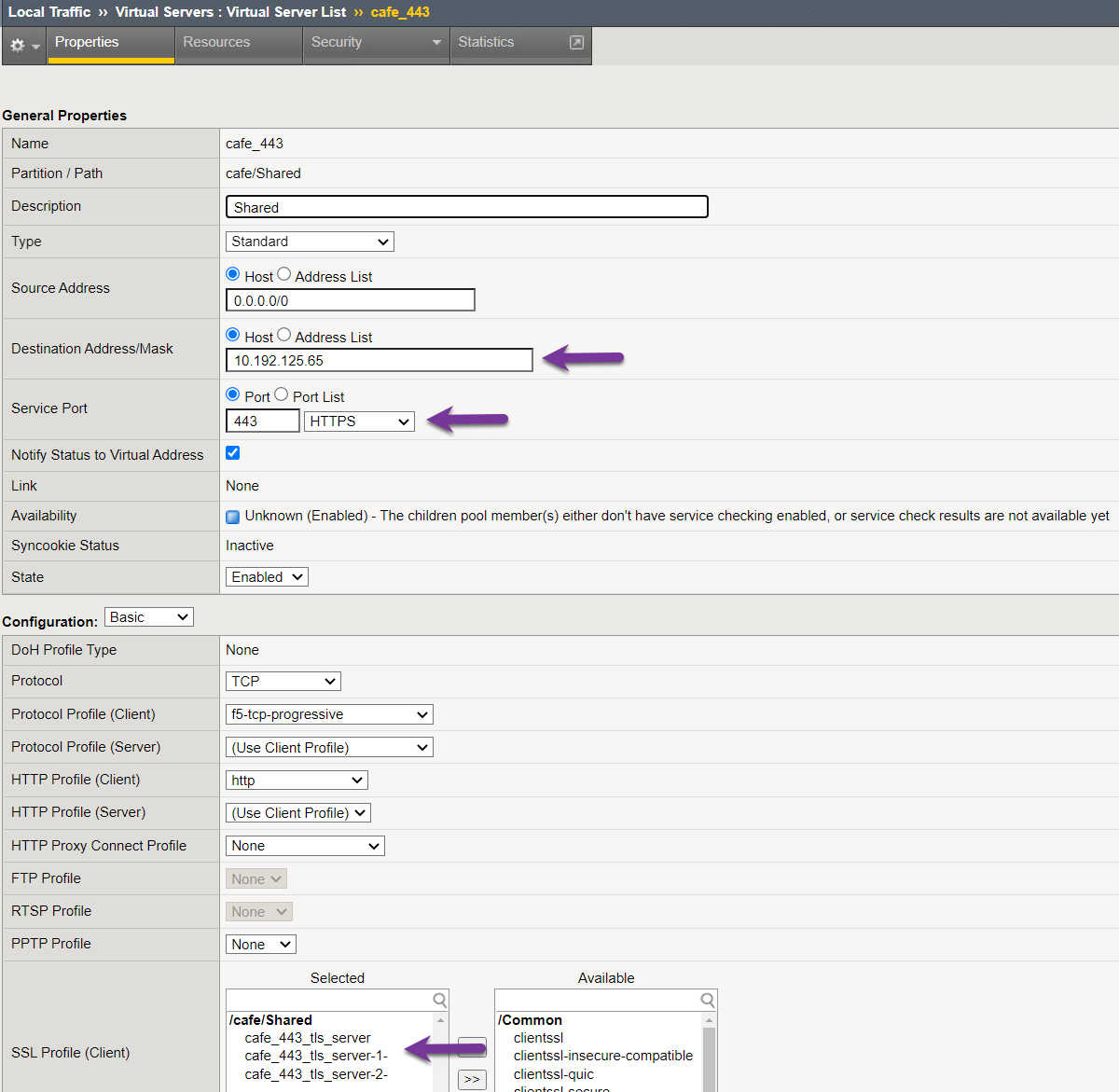
Step 2: Validate OpenShift Virtual IP using the BIG-IP¶
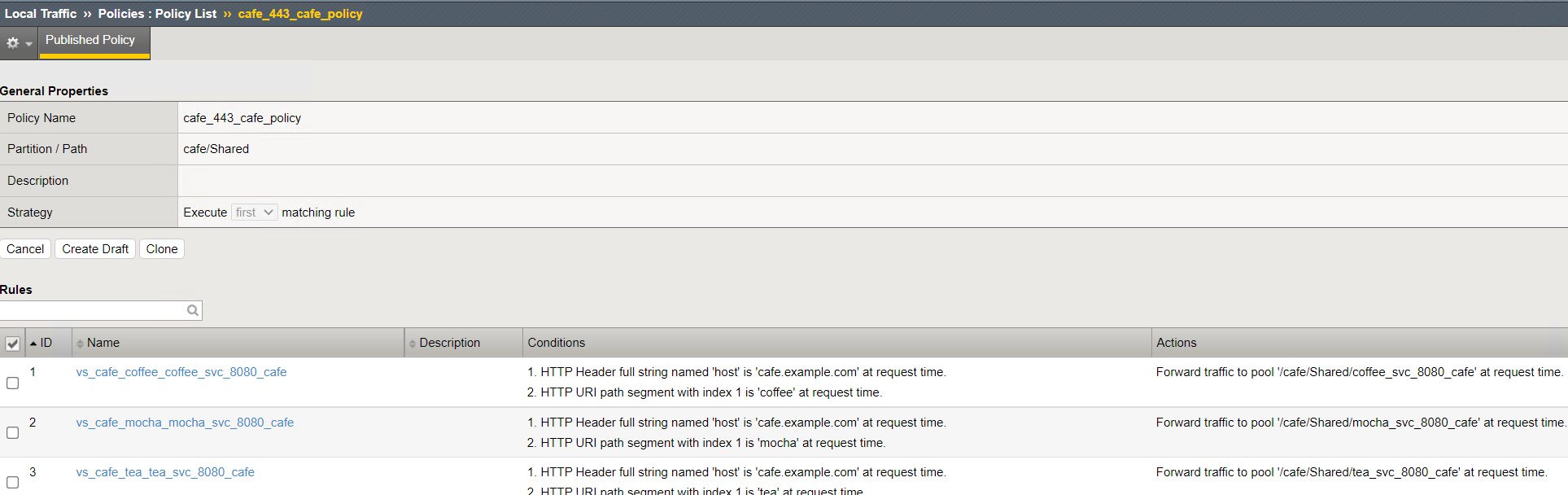
Step 3: Validate OpenShift Routes policies on the BIG-IP¶
Step 4: Validate OpenShift Routes policies by connecting to the Public IP¶
Note
To provide feedback on Container Ingress Services or this documentation, please file a GitHub Issue.