CIS Installation¶
Overview¶
CIS can be configured in multiple ways depending on the customer scenario. CIS can be deployed on Kubernetes and OpenShift platform. CIS installation may differ based on the resources (for example: ConfigMap, Ingress, Routes, and CRD) used by the customer to expose the Kubernetes services. CIS installation also depends on BIG-IP deployment (stand alone and HAproxy configuration) and Kubernetes cluster networking (Flannel/Calico).
Prerequisites¶
These are the mandatory requirements for deploying CIS:
OpenShift/Kubernetes Cluster must be up and running.
AS3: 3.18+ must be installed on your BIG-IP system.
Use the latest TLS version and cipher suites in Kubernetes for kube-api.
Create a BIG-IP partition to manage Kubernetes objects. This partition can be created either via the GUI (System > Users > Partition List) or via our TMOS CLI:
create auth partition <cis_managed_partition>
You need a user with administrative access to this partition.
If you need to pull the k8s-bigip-ctlr image from a private Docker registry, store your Docker login credentials as a Secret.
Additionally, if you are deploying CIS in Cluster Mode you need to have following prerequisites. For more information, see Deployment Options.
- You must have a fully active/licensed BIG-IP. SDN must be licensed. For more information, see BIG-IP VE license support for SDN services.
- VXLAN tunnel should be configured from OpenShift/Kubernetes Cluster to BIG-IP. For more information, see Creating VXLAN Tunnels.
Installing CIS Using Helm Charts¶
This is the simplest way to install CIS on OpenShift/Kubernetes cluster. Helm is a package manager for Kubernetes. Helm is Kubernetes version of yum or apt. Helm deploys something called charts, which you can think of as a packaged application. It is a collection of all your versioned, pre-configured application resources which can be deployed as one unit.
Optionally, add BIG-IP credentials as K8S secrets.
For Kubernetes, use the following command:
kubectl create secret generic bigip-login -n kube-system --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=<password>
For Openshift, use the following command:
oc create secret generic bigip-login -n kube-system --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=<password>
Add the CIS chart repository in Helm using following command:
helm repo add f5-stable https://f5networks.github.io/charts/stable
Create values.yaml as shown below:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 | bigip_login_secret: f5-bigip-ctlr-login bigip_secret: create: false username: password: rbac: create: true serviceAccount: # Specifies whether a service account should be created create: true # The name of the service account to use. # If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template name: k8s-bigip-ctlr # This namespace is where the Controller lives; namespace: kube-system ingressClass: create: true ingressClassName: f5 isDefaultIngressController: true args: # See https://clouddocs.f5.com/containers/latest/userguide/config-parameters.html # NOTE: helm has difficulty with values using `-`; `_` are used for naming # and are replaced with `-` during rendering. # REQUIRED Params bigip_url: <ip_address-or-hostname> bigip_partition: <name_of_partition> # OPTIONAL PARAMS -- uncomment and provide values for those you wish to use. # verify_interval: # node-poll_interval: # log_level: # python_basedir: ~ # VXLAN # openshift_sdn_name: # flannel_name: # KUBERNETES # default_ingress_ip: # kubeconfig: # namespaces: ["foo", "bar"] # namespace_label: # node_label_selector: # pool_member_type: nodeport # resolve_ingress_names: # running_in_cluster: # use_node_internal: # use_secrets: # insecure: true # custom-resource-mode: true # log-as3-response: true # gtm-bigip-password # gtm-bigip-url # gtm-bigip-username # ipam : true image: # Use the tag to target a specific version of the Controller user: f5networks repo: k8s-bigip-ctlr pullPolicy: Always version: latest # affinity: # nodeAffinity: # requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: # nodeSelectorTerms: # - matchExpressions: # - key: kubernetes.io/arch # operator: Exists # securityContext: # runAsUser: 1000 # runAsGroup: 3000 # fsGroup: 2000 # If you want to specify resources, uncomment the following # limits_cpu: 100m # limits_memory: 512Mi # requests_cpu: 100m # requests_memory: 512Mi # Set podSecurityContext for Pod Security Admission and Pod Security Standards # podSecurityContext: # runAsUser: 1000 # runAsGroup: 1000 # privileged: true |
Installing Helm charts:
Install the Helm chart using the following command if BIG-IP credential secrets are created manually:
helm install -f values.yaml <new-chart-name> f5-stable/f5-bigip-ctlr
Install the Helm chart with
--skip crdsif BIG-IP credential secrets are created manually (without Custom Resource Definitions installations):helm install --skip-crds -f values.yaml <new-chart-name> f5-stable/f5-bigip-ctlr
If you want to create the BIG-IP credential secret with Helm charts, use the following command:
helm install --set bigip_secret.create="true" --set bigip_secret.username=$BIGIP_USERNAME --set bigip_secret.password=$BIGIP_PASSWORD -f values.yaml <new-chart-name> f5-stable/f5-bigip-ctlr
Note
For Kubernetes versions lower than 1.18, please use Helm chart version 0.0.14 as follows: helm install --skip-crds -f values.yaml <new-chart-name> f5-stable/f5-bigip-ctlr --version 0.0.14.
Chart parameters¶
| Parameter | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| bigip_login_secret | Optional | f5-bigip-ctlr-login | Secret that contains BIG-IP login credentials. |
| bigip_secret.create | Optional | false | Create Kubernetes secret using username and password. |
| bigip_secret.username | Optional | N/A | BIG-IP username to create the Kubernetes secret. |
| bigip_secret.password | Optional | N/A | BIG-IP password to create the Kubernetes secret. |
| args.bigip_url | Required | N/A | The management IP for your BIG-IP device. |
| args.bigip_partition | Required | f5-bigip-ctlr | BIG-IP partition the CIS Controller will manage. |
| args.namespaces | Optional | N/A | List of Kubernetes namespaces which CIS will monitor. |
| rbac.create | Optional | true | Create ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding. |
| serviceAccount.name | Optional | f5-bigip-ctlr- serviceaccount | Name of the ServiceAccount for CIS controller. |
| serviceAccount.create | Optional | true | Create service account for the CIS controller. |
| namespace | Optional | kube-system | Name of namespace CIS will use to create deployment and other resources. |
| image.user | Optional | f5networks | CIS Controller image repository username. |
| image.repo | Optional | k8s-bigip-ctlr | CIS Controller image repository name. |
| image.pullPolicy | Optional | Always | CIS Controller image pull policy. |
| image.pullSecrets | Optional | N/A | List of secrets of container registry to pull image. |
| version | Optional | latest | CIS Controller image tag. |
| nodeSelector | Optional | N/A | Dictionary of Node selector labels. |
| tolerations | Optional | N/A | Array of labels. |
| limits_cpu | Optional | 100m | CPU limits for the pod. |
| limits_memory | Optional | 512Mi | Memory limits for the pod. |
| requests_cpu | Optional | 100m | CPU request for the pod. |
| requests_memory | Optional | 512Mi | Memory request for the pod. |
| affinity | Optional | N/A | Dictionary of affinity. |
| securityContext | Optional | N/A | Dictionary of deployment securityContext. |
| podSecurityContext | Optional | N/A | Dictionary of pod securityContext. |
| ingressClass.ingressClassName | Optional | f5 | Name of ingress class. |
| ingressClass.isDefaultIngressController | Optional | false | CIS will monitor all the ingress resources if set true. |
| ingressClass.create | Optional | true | Create ingress class. |
Note
The parameters bigip_login_secret and bigip_secret are mutually exclusive. If both are defined in the values.yaml file, bigip_secret will be given priority.
Uninstalling Helm Chart¶
Run the following command to uninstall the chart.
helm uninstall <new-chart>
Installing CIS Manually¶
Add BIG-IP credentials as K8S secrets.
- For Kubernetes, use the following command:
kubectl create secret generic bigip-login -n kube-system --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=<password>
- For Openshift, use the following command:
oc create secret generic bigip-login -n kube-system --from-literal=username=admin --from-literal=password=<password>
Create a service account for deploying CIS.
- For Kubernetes, use the following command:
kubectl create serviceaccount bigip-ctlr -n kube-system
- For Openshift, use the following command:
oc create serviceaccount bigip-ctlr -n kube-system
Fetch the latest RBAC for both Kubernetes and Openshift.
- For Kubernetes, use the following command.
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/F5Networks/k8s-bigip-ctlr/2.x-master/docs/config_examples/rbac/k8s_rbac.yml
- For Openshift, use the following command.
oc create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/F5Networks/k8s-bigip-ctlr/2.x-master/docs/config_examples/rbac/openshift_rbac.yaml
For Openshift, you need to create the Cluster admin privileges for the BIG-IP service account user with the following command:
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-admin -z bigip-ctlr -n kube-system
Create a CIS deployment using cis_deploy.yaml as shown below:
For Kubernetes, use the following command:
kubectl apply -f cis_deploy.yaml
For Openshift, use the following command:
oc apply -f cis_deploy.yaml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 | apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: k8s-bigip-ctlr-deployment namespace: kube-system spec: # DO NOT INCREASE REPLICA COUNT replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: k8s-bigip-ctlr-deployment template: metadata: labels: app: k8s-bigip-ctlr-deployment spec: # Name of the Service Account bound to a Cluster Role with the required # permissions containers: - name: k8s-bigip-ctlr image: "f5networks/k8s-bigip-ctlr:latest" env: - name: BIGIP_USERNAME valueFrom: secretKeyRef: # Replace with the name of the Secret containing your login # credentials name: bigip-login key: username - name: BIGIP_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: # Replace with the name of the Secret containing your login # credentials name: bigip-login key: password command: ["/app/bin/k8s-bigip-ctlr"] args: [ # See the k8s-bigip-ctlr documentation for information about # all config options # When insecure=true, this enables insecure SSL communication to the BIG-IP system." # https://clouddocs.f5.com/containers/latest/userguide/config-parameters.html "--bigip-username=$(BIGIP_USERNAME)", "--bigip-password=$(BIGIP_PASSWORD)", "--bigip-url=<ip_address-or-hostname>", "--bigip-partition=<name_of_partition>", "--pool-member-type=nodeport", "--insecure", ] serviceAccountName: bigip-ctlr |
Installing CIS using Operators on OpenShift Cluster¶
An Operator is a method of packaging, deploying, and managing a Kubernetes application. A Kubernetes application is an application that is both deployed on Kubernetes and managed using the Kubernetes APIs and kubectl/oc tooling. You can think of Operators as the runtime that manages this type of application on Kubernetes. Conceptually, an Operator takes human operational knowledge and encodes it into software that is more easily packaged and shared with consumers.
The F5 BIG-IP CIS (k8s-bigip-ctlr) is a cloud-native connector that can use either Kubernetes or OpenShift as a BIG-IP orchestration platform. F5 BIG-IP CIS Operator is a Service Operator which installs F5 BIG-IP CIS on OpenShift platforms 4.x.
Before you install CIS using Operators on OpenShift, you must create BIG-IP login credentials to use with Operator Helm Charts:
oc create secret generic <SECRET-NAME> -n kube-system
--from-literal=username=<USERNAME> --from-literal=password=<PASSWORD>
Access the OCP web console: From CLI, login as admin using CRC given credentials. In the example below, the username is
kubeadminand the password isdb9Dr-J2csc-8oP78-9sbmf.$ eval $(crc oc-env) $ oc login -u kubeadmin -p db9Dr-J2csc-8oP78-9sbmf https://api.crc.testing:6443
Within the OCP web console, in the left Menu bar, click Operator Hub and search for “f5” to see the Certified F5 BIG-IP CIS Operator.
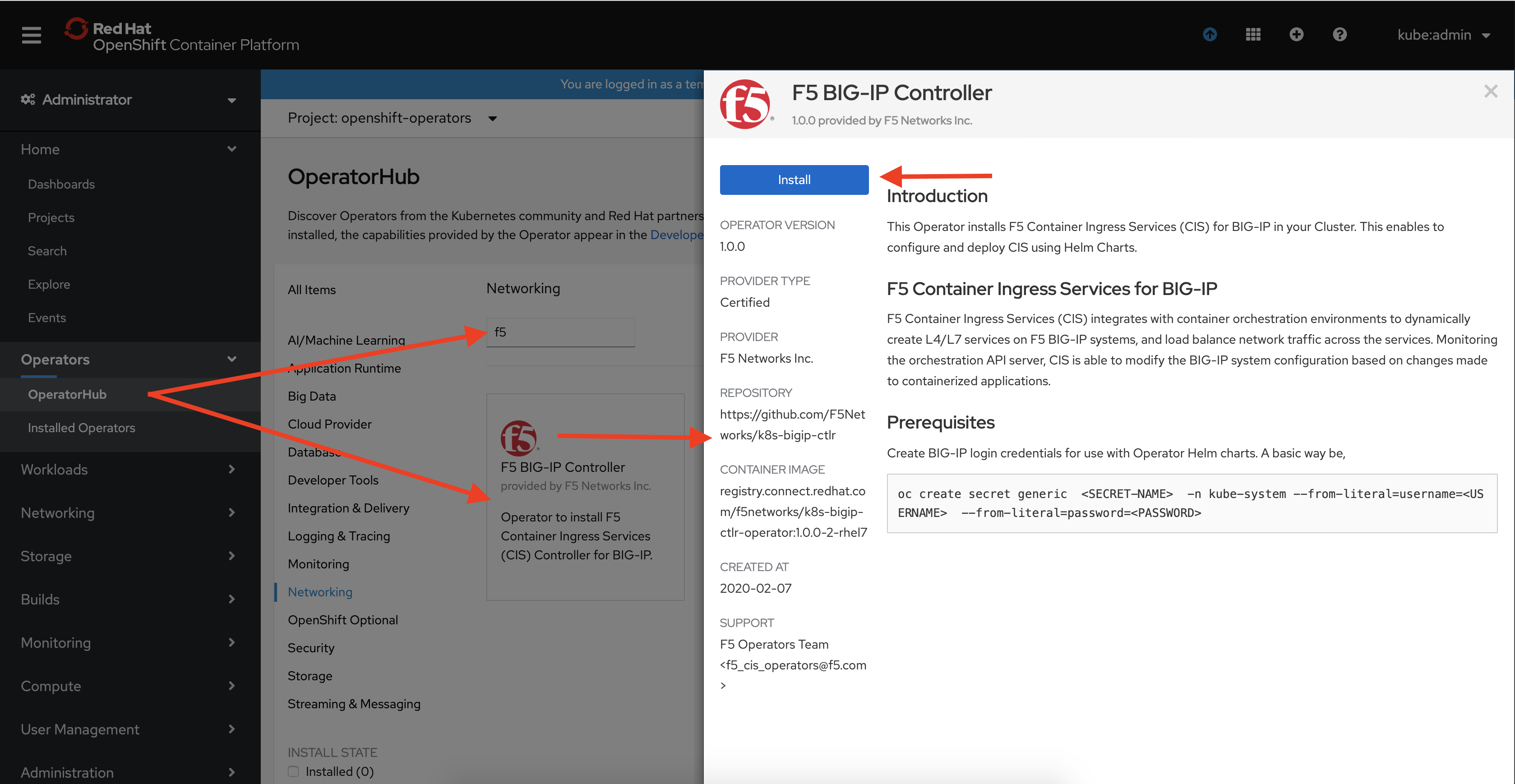
Click Install to go through the guided installation process.
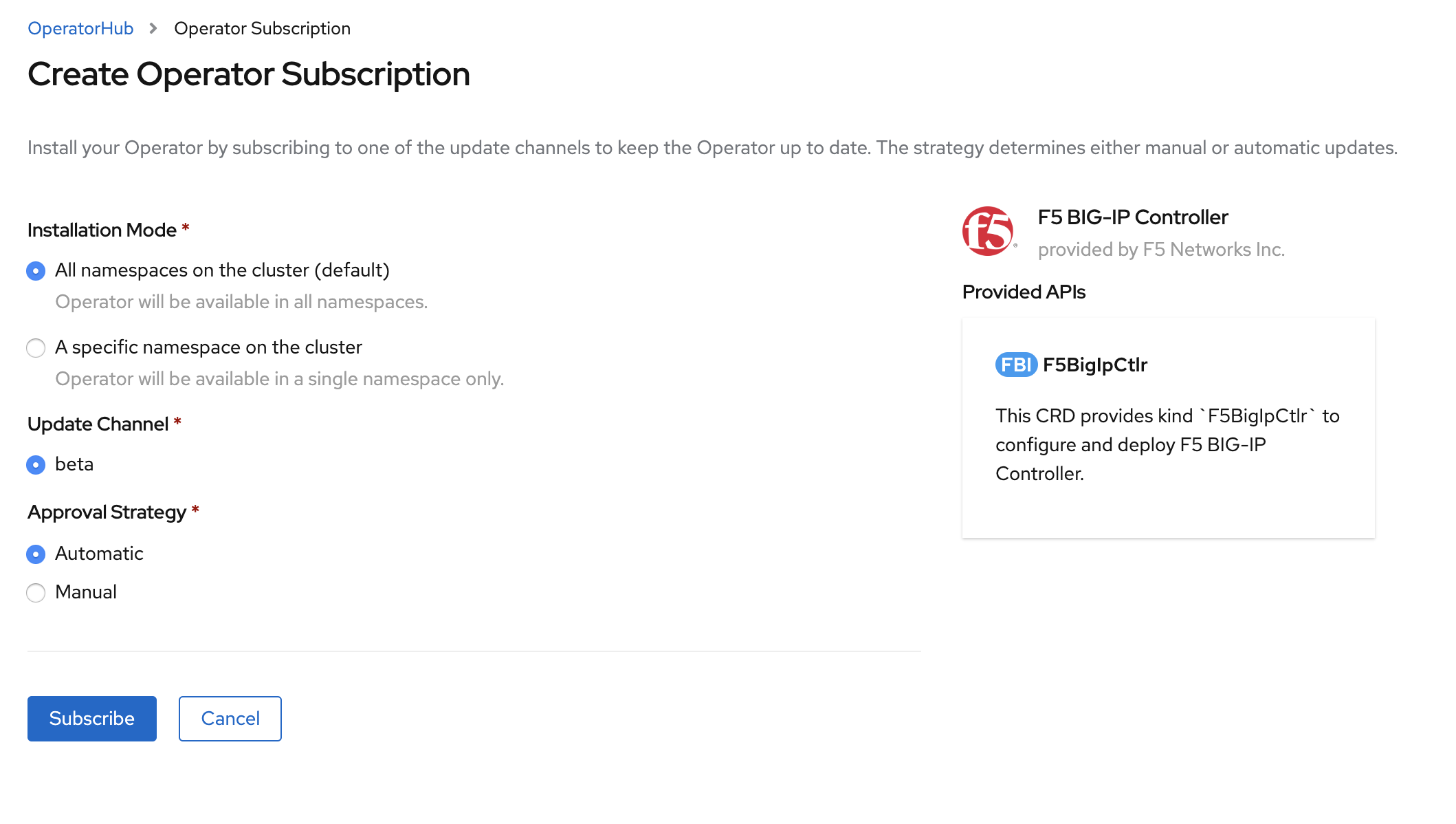
When Operator is Subscribed, Operator is installed based on approval strategy. The default approval strategy is Automatic.
- Manual: Requires administrator approval to install new updates.
- Automatic: When a new release is available, updated automatic.
Creating VXLAN Tunnels¶
Creating VXLAN Tunnels on Kubernetes Cluster¶
This configuration is for Standalone BIG-IP.
Log in to BIG-IP and create a partition called kubernetes for CIS.
tmsh create auth partition kubernetes
Create a VXLAN profile.
tmsh create net tunnels vxlan fl-vxlan port 8472 flooding-type none
Create a VXLAN tunnel.
tmsh create net tunnels tunnel fl-vxlan key 1 profile fl-vxlan local-address 10.1.1.4
Create the VXLAN tunnel self IP.
tmsh create net self 10.1.1.4 address 10.244.20.4/255.255.0.0 allow-service none vlan fl-vxlan
Save the configuration.
tmsh save sys config
Before deploying CIS in ClusterIP mode, you need to configure BIG-IP as a node in the Kubernetes cluster. To do so you will need to modify
bigip-node.yamlwith the MAC address auto-created from the previous steps. From the jumpbox terminal, run the following command atbigip1. Copy the displayed MAC Address.tmsh show net tunnels tunnel k8s-tunnel all-properties
Update the MAC address obtained in the previous step to the following YAML file:
bigip-node.yaml¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
apiVersion: v1 kind: Node metadata: name: bigip1 annotations: #Replace IP with self IP for your deployment flannel.alpha.coreos.com/public-ip: "10.1.1.4" #Replace MAC with your BIG-IP Flannel VXLAN Tunnel MAC flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-data: '{"VtepMAC":"2c:c2:60:23:0c:58"}' flannel.alpha.coreos.com/backend-type: "vxlan" flannel.alpha.coreos.com/kube-subnet-manager: "true" spec: #Replace Subnet with your BIG-IP Flannel Subnet podCIDR: "10.244.20.0/24"
Create the BIG-IP node:
kubectl create -f bigip-node.yaml
Verify “bigip1” node is created:
kubectl get nodes
Creating VXLAN Tunnels on Openshift Cluster¶
This configuration is for Standalone BIG-IP.
Log in to the BIG-IP and create net tunnels vxlan vxlan-mp flooding-type multipoint on BIG-IP.
create net tunnels vxlan vxlan-mp flooding-type multipoint
create net tunnels tunnel openshift_vxlan key 0 profile vxlan-mp local-address 10.1.1.4
Add the BIG-IP device to the OpenShift overlay network.
create net self 10.131.0.83/14 allow-service all vlan openshift_vxlan
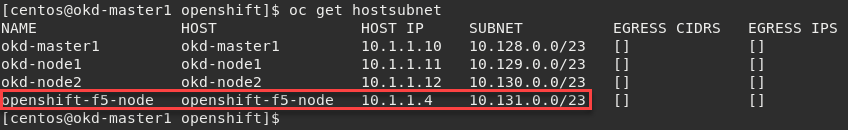
Create a new HostSubnet for BIG-IP on the OpenShift/Kubernetes cluster. This will provide the subnet for creating the tunnel self IP.
oc create -f openshift-hostsubnet.yaml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | apiVersion: network.openshift.io/v1 kind: HostSubnet metadata: name: openshfit-f5-node annotations: pod.network.openshift.io/fixed-vnid-host: "0" pod.network.openshift.io/assign-subnet: "true" # provide a name for the node that will serve as BIG-IP's entry into the cluster host: openshfit-f5-node # The hostIP address will be the BIG-IP interface address routable to the # OpenShift Origin nodes. # This address is the BIG-IP VTEP in the SDN's VXLAN. hostIP: 10.1.1.4 subnet: "10.131.0.0/23" |
Note
To provide feedback on Container Ingress Services or this documentation, please file a GitHub Issue.