F5 Application Delivery Controller Solutions > Resilient Data Center Architectures with F5 BIG-IP Source | Edit on
Getting Started¶
You will be using an ssh client to access all components of this lab. All configuration will be done via the CLI.
Please follow the instructions provided by the instructor to start your lab and access your jump host.
Note
All work for this lab will be performed exclusively from the Linux Jumphost via ssh.
- No installation or interaction with your local system is required. If you do not have an ssh client you can install the freeware putty.
- https://putty.org
Lab Topology¶
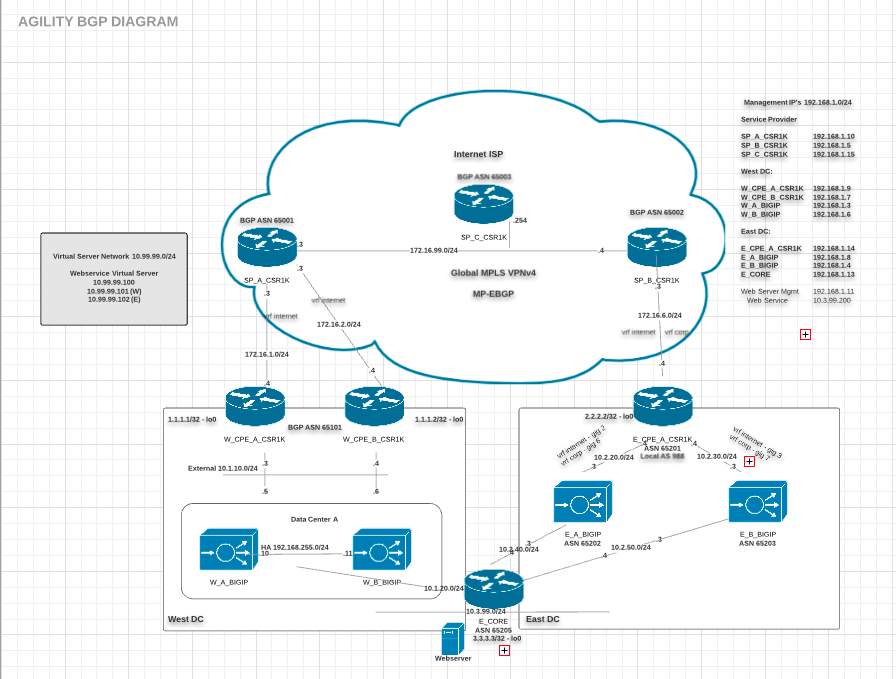
The following components have been included in your lab environment:
- 4 x F5 BIG-IP VE (v13.1)
- 7 x CSR 1000v Virtual Routers
- 1 x Linux Webserver (xubuntu 14.04)
- 1 x Linux Jumphost
Lab Components¶
The following table lists the management IP Addresses and Credentials for all components:
| Host | Management IP | Credentials |
|---|---|---|
| Linux Jumphost | <Public IP on worksheet> | ubuntu:Agility2018f5 |
| W_A_BIGIP | 192.168.1.3 | root:default |
| W_B_BIGIP | 192.168.1.6 | root:default |
| W_CPE_A_CSR1K | 192.168.1.9 | root:default |
| W_CPE_B_CSR1K | 192.168.1.7 | root:default |
| E_A_BIGIP | 192.168.1.8 | root:default |
| E_B_BIGIP | 192.168.1.4 | root:default |
| E_CPE_A_CSR1K | 192.168.1.14 | root:default |
| SP_A_CSR1K | 192.168.1.10 | root:default |
| SP_B_CSR1K | 192.168.1.5 | root:default |
| SP_C_CSR1K | 192.168.1.15 | root:default |
| Web Service | 10.3.99.200 |
Note
Additional Credentials - enable password or priveleged mode on the CSR1000v routers: san-fran
Priveleged mode allows you to run commands that might be disruptive to network traffic or enter configuration mode.
BIG-IP CLI Primer¶
bash shell¶
Default linux shell when you log in to the BIG-IP as root
Common commands you can run from here:
- ping
- traceroute
- tcpdump
- imish (used to access the ZebOS router shell)
- tmsh (used to access the traffic management shell for BIG-IP configuration)
tm shell (tmsh)¶
From bash any command you know the syntax of can be entered directly by preceding it with the 'tmsh' command
For context based help and tab completion you can enter the 'tmsh' command and go directly to the prompt.
Using the '?' for context aware help
admin@(BIGIP131)(cfg-sync In Sync)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# create ltm ?
Modules:
auth Virtual server authentication configuration
cipher Cipher Rule and Group configuration
classification Traffic Classification
data-group Data group configuration
dns DNS configuration
html-rule Generalized HTML rule-based patcher
message-routing Message routing framework configuration
monitor LTM monitor templates
persistence Virtual server persistence configuration
profile Virtual server profile configuration
tacdb TACDB configuration.
Components:
eviction-policy Defines an eviction policy, used to select which flows to evict when approaching limits.
ifile iFile Configuration
nat Network address translation configuration
node Node specific pool member configuration
policy Centralized Policy Matching configuration
policy-strategy Centralized Policy Matching rule selection strategy
pool Load balancing pool configuration
rule iRules configuration
rule-profiler
snat Secure network address translation (SNAT) configuration
snat-translation SNAT translation address configuration
snatpool Collections of SNAT translation addresses
traffic-class Traffic Class Configuration
virtual Virtual server configuration
virtual-address Virtual server IP address configuration
Using 'tab' to offer possible completions
admin@(BIGIP131)(cfg-sync In Sync)(Active)(/Common)(tmos)# create ltm
Modules:
auth classification dns message-routing persistence tacdb
cipher data-group html-rule monitor profile
Components:
eviction-policy nat policy pool rule-profiler snat-translation traffic-class virtual-address
ifile node policy-strategy rule snat snatpool virtual
By partially typing a keyword you can use 'tab' to either auto-complete or give you the list of options.
To exit the tmsh shell just type 'quit':
ZebOS router shell (imish)¶
From the BIG-IP bash cli you can enter the ZebOS router shell by typing the command 'imish'. If you have multiple route domains, you can specify which by adding the '-r #'
Route domain '0' is default.
From there you can enter priveleged mode which will allow you do run administrative level commands and also enter in to the configuration mode.
Note how the prompt changes from '>' to '#'. This is how you can determine which mode you are in. If a command fails, it may be because you do not have sufficient priveleges. There is no enable password on the ZebOS instances for this lab.
From priveleged mode, you can type 'configure terminal' to enter configuration mode. You can shorten this as shown below with the command 'config t' as you will see often in this lab.
Note
Cisco devices in this lab behave similar to the ZebOS cli with the exception of requiring a secondary enable password to access priveleged mode.