Advanced Multi-layer Firewall Protection > Advanced Multi-Layer Firewall Protection > Module 1: F5 Multi-layer Firewall Source | Edit on
Lab 5: Provide Firewall Security Policies For CDN Enabled Applications¶
Many enterprise sites have some or all of their content served up by Content Delivery Networks (CDN). This common use case leverages proxies to provide static content closer to the end client machines for performance. Because of this there may only be one or two IP addresses connecting to the origin website. The original IP address of the client in this case is often mapped to a common HTTP header X-Forwarded-For or some variation. In this deployment, the BIG-IP can translate the original source of the request in the XFF to the source IP address.
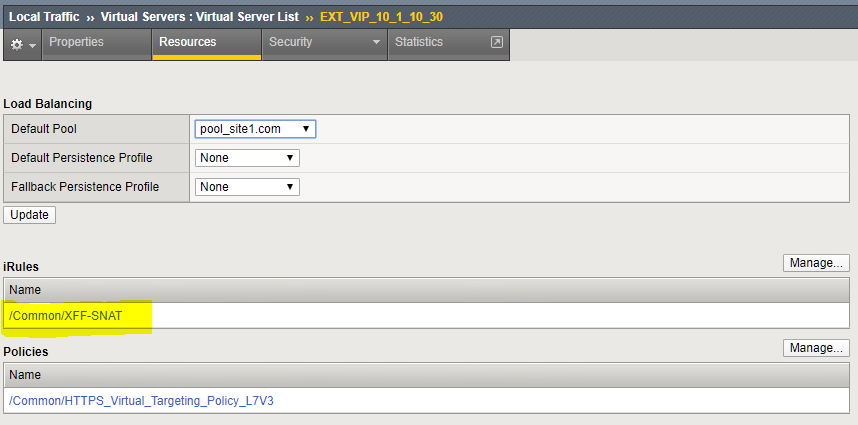
In this case we are going to leverage iRules to modify the traffic coming from the CDN networks so we can apply a firewall policy to it. The iRule to accomplish this is already installed on your BIG-IP and applied to EXT_VIP_10_1_10_30. We have been leveraging it to run the tests in previous exercises.
The iRule syntax is as follows:
Examining the iRule we find that it is called when an HTTP request
happens. It then checks to see if the X-Forwarded-For header
exists (We wouldn’t want to SNAT to a non-existent IP address) and
if it does it modifies the source IP address of the request to the
IP address provided in the header.
Verify that the iRule is assigned to the Virtual Server¶
- Navigate to Local Traffic > Virtual Servers.
- Click on the EXT_VIP_10.1.10.30 virtual server, then click on the Resources tab.
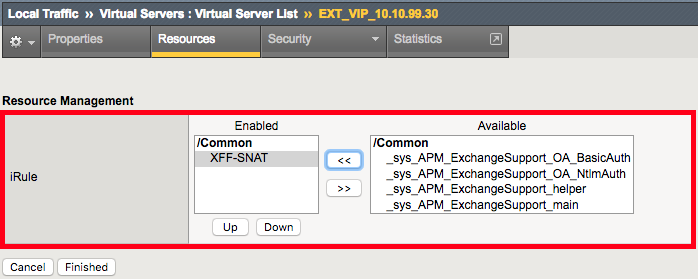
- Click on the Manage button next to iRules. This is to show you where iRules are assigned to virtual servers.
- Click on the Cancel button since the iRule is already assigned.
Validate SNAT Function¶
Let’s once again leverage curl from the Cygwin Terminal to insert the X-Forwarded-For header in to the request.
Expected Result: The site should be blocked by the geo_restrict_rule_list.
Now, validate that requests sourced from the X-Forwarded-For IP address of 172.16.99.5 are allowed.
Expected Result: Site’s main page is retrieved.
Solve For TCP Issues With CDN Networks¶
The next step is to solve for the TCP connection issue with CDN providers. While we are provided the originating client IP address to allow/drop traffic, simply dropping or resetting the connection can be problematic for other users of the application.
Instead of dropping the connection immediately, we can send an HTTP 403 response. This more graceful solution is accomplished via AFM iRules. The iRule has already been created. We need to apply it to the downloads_policy policy. It still is logged as a drop or reset in the firewall logs. We allow it to be processed slightly further so that a Layer 7 response can be provided.
Return to the BIG-IP TMUI in Chrome.
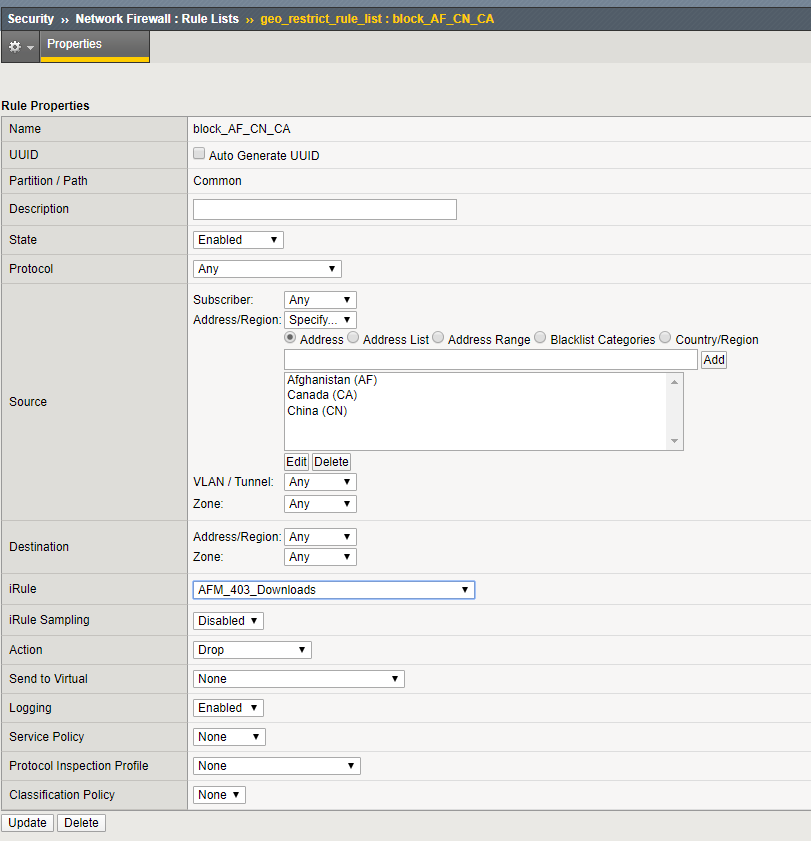
- Navigate to Security > Network Firewall > Rule Lists.
- Select geo_restrict_rule_list, then select block_AF_CN_CA.
- Add the AFM_403_Downloads iRule to the rule list, then click Update.
- Validate that denied requests are now responded with a Layer 7 403 Error Page.
Expected Result: Instead of the traffic getting dropped, a 403 error should be returned as shown below.
This concludes Module 1 - Lab 5. Click Next to continue.